On 11 September 2004 the island of Grand Cayman, which lies largely unprotected at sea level, was hit by Hurricane Ivan, creating an 8-ft (2.4 m) storm surge which flooded many areas of Grand Cayman. An estimated 83% of the dwellings on the island were damaged including 4% requiring complete reconstruction. A reported 70% of all dwellings suffered severe damage from flooding or wind. Another 26% sustained minor damage from partial roof removal, low levels of flooding, or impact with floating or wind driven hurricane debris. Power, water and communications were disrupted for months in some areas as Ivan was the worst hurricane to hit the islands in 86 years. Grand Cayman began a major rebuilding process and within two years its infrastructure was nearly returned to pre-hurricane status. Due to the tropical location of the islands, more hurricanes or tropical systems have affected the Cayman Islands than any other region in the Atlantic basin; it has been brushed or directly hit, on average, every 2.23 years.
Geography:
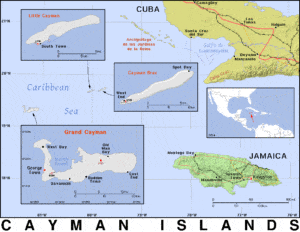
The islands are in the western Caribbean Sea and are the peaks of an undersea mountain range called the Cayman Ridge (or Cayman Rise). This ridge flanks the Cayman Trough, 6,000 m (20,000 ft) deep which lies 6 km (3.7 mi) to the south. The islands lie in the northwest of the Caribbean Sea, east of Quintana Roo, Mexico and Yucatán State, Mexico, northeast of Costa Rica, north of Panama, south of Cuba and west of Jamaica. They are situated about 700 km (430 mi) south of Miami, 750 km (470 mi) east of Mexico, 366 km (227 mi) south of Cuba,[28] and about 500 km (310 mi) northwest of Jamaica. Grand Cayman is by far the largest, with an area of 197 km2 (76 sq mi). Grand Cayman’s two “sister islands”, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, are about 120 km (75 mi) east north-east of Grand Cayman and have areas of 38 and 28.5 km2 (14.7 and 11.0 sq mi) respectively. The nearest land mass from Grand Cayman is the Canarreos Archipelago (about 240 km or 150 miles away), whereas the nearest from the easternmost island Cayman Brac is the Jardines de la Reina archipelago (about 160 km or 100 miles away) – both of which are part of Cuba.
All three islands were formed by large coral heads covering submerged ice-age peaks of western extensions of the Cuban Sierra Maestra range and are mostly flat. One notable exception to this is The Bluff on Cayman Brac’s eastern part, which rises to 43 m (141 ft) above sea level, the highest point on the islands.
Terrain is mostly a low-lying limestone base surrounded by coral reefs.
Economy:
The economy of the Cayman Islands is dominated by financial services and tourism, together accounting for 50-60% of Gross Domestic Product. The nation’s low tax rates have led to it being used as a tax haven for corporations; there are 100,000 companies registered in the Cayman Islands, more than the population itself. The Cayman Islands have come under criticism for allegations of money laundering and other financial crimes, including a 2016 statement by former US president Barack Obama of a particular building as “tax scam” for housing 12,000 corporations.


