Introduction:
Alaska is a U.S. state in the northwest extremity of North America.
The Canadian administrative divisions of British Columbia and Yukon border the state to the east, its most extreme western part is Attu Island, and it has a maritime border with Russia (Chukotka Autonomous Okrug) to the west across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort seas—the southern parts of the Arctic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest.
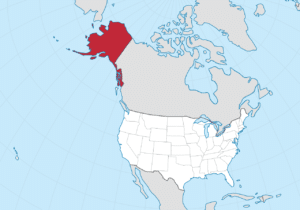
It is the largest state in the United States by area.
Approximately half of Alaska’s residents live within the Anchorage metropolitan area.

Alaska’s economy is dominated by the fishing, natural gas, and oil industries, resources which it has in abundance. Military bases and tourism are also a significant part of the economy.
Origin of the Name:
The name “Alaska” (Russian: Аляска, tr. Alyaska) was introduced in the Russian colonial period when it was used to refer to the Alaska Peninsula. It was derived from an Aleut-language idiom, which figuratively refers to the mainland. Literally, it means object to which the action of the sea is directed.
Geography:
Alaska is the northernmost and westernmost state in the United States and has the most easterly longitude in the United States because the Aleutian Islands extend into the Eastern Hemisphere. Alaska is the only non-contiguous U.S. state on continental North America; about 500 miles of British Columbia, Canada, separates Alaska from Washington. It is technically part of the continental U.S., but is sometimes not included in colloquial use; Alaska is not part of the contiguous U.S., often called “the Lower 48”. The capital city, Juneau, is situated on the mainland of the North American continent but is not connected by road to the rest of the North American highway system.
Alaska’s territorial waters touch Russia’s territorial waters in the Bering Strait, as the Russian Big Diomede Island and Alaskan Little Diomede Island are only 3 miles apart. Alaska has a longer coastline than all the other U.S. states combined.
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by total area at 663,268 square miles, over twice the size of Texas, the next largest state.
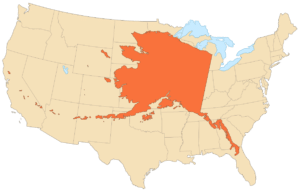
Alaska is larger than all but 18 sovereign countries. Counting territorial waters, Alaska is larger than the combined area of the next three largest states: Texas, California, and Montana. It is also larger than the combined area of the 22 smallest U.S. states.
Regions:
South Central:
The South Central region is the most populous region of Alaska, containing Anchorage, the Matanuska-Susitna Valley and the Kenai Peninsula. Rural, mostly unpopulated areas south of the Alaska Range and west of the Wrangell Mountains also fall within the definition of South Central, as do the Prince William Sound area and the communities of Cordova and Valdez.
Southeast:
Also referred to as the Panhandle or Inside Passage, this is the region of Alaska closest to the rest of the United States. As such, this was where most of the initial non-indigenous settlement occurred in the years following the Alaska Purchase. The region is dominated by the Alexander Archipelago as well as the Tongass National Forest, the largest national forest in the United States. It contains the state capital Juneau, the former capital Sitka, and Ketchikan, at one time Alaska’s largest city.
