Introduction:
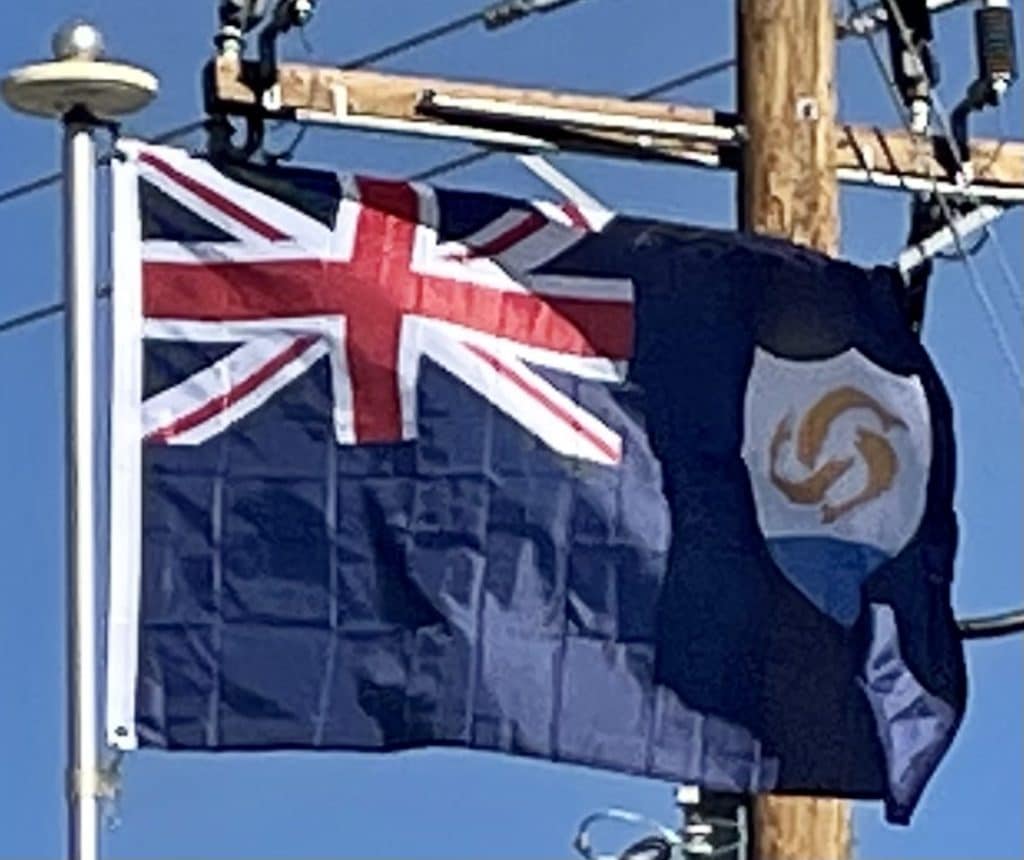
Anguilla is a British overseas territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin.
The territory consists of the main island of Anguilla, approximately 16 miles (26 kilometers) long by 3 miles (5 km) wide at its widest point, together with a number of much smaller islands and cays with no permanent population. The territory’s capital is The Valley. The total land area of the territory is 35 square miles (91 km2), with a population of approximately 14,731 (2018).
History:
Precisely when Anguilla was first seen by Europeans is uncertain: some sources claim that Columbus sighted the island during his second voyage in 1493, while others state that the first European explorer was the French Huguenot nobleman and merchant René Goulaine de Laudonnière in 1564. The Dutch West India Company established a fort on the island in 1631. However, the Company later withdrew after its fort was destroyed by the Spanish in 1633.
Traditional accounts state that Anguilla was first colonized by English settlers from Saint Kitts beginning in 1650. The settlers focused on planting tobacco, and to a lesser extent cotton. The French temporarily took over the island in 1666 but returned it to English control under the terms of the Treaty of Breda the next year. Major John Scott who visited in September 1667, wrote of leaving the island “in good condition” and noted that in July 1668, “200 or 300 people fled thither in time of war”. The French attacked again in 1688, 1745 and 1798, causing much destruction but failing to capture the island.
It is likely that the early European settlers brought enslaved Africans with them. Historians confirm that African slaves lived in the region in the early 17th century, such as slaves from Senegal living on St Kitts in the mid 1600s. By 1672 a slave depot existed on the island of Nevis, serving the Leeward Islands. While the time of African arrival in Anguilla is difficult to place precisely, archival evidence indicates a substantial African presence of at least 100 enslaved people by 1683; these seem to have come from Central Africa as well as West Africa. The slaves were forced to work on the sugar plantations which had begun to replace tobacco as Anguilla’s main crop. Over time the African slaves and their descendants came to vastly outnumber the white settlers. The African slave trade was eventually terminated within the British Empire in 1807, and slavery outlawed completely in 1834. Many planters subsequently sold up or left the island.
During the early colonial period, Anguilla was administered by the British through Antigua; in 1825, it was placed under the administrative control of nearby Saint Kitts. Anguilla was federated with St Kitts and Nevis in 1882, against the wishes of many Anguillans. Economic stagnation, and the severe effects of several droughts in the 1890s and later the Great Depression of the 1930s led many Anguillans to emigrate for better prospects elsewhere.

