In 1045, the Byzantine Empire conquered Bagratid Armenia. Soon, the other Armenian states fell under Byzantine control as well. The Byzantine rule was short lived, as in 1071 the Seljuk Empire defeated the Byzantines and conquered Armenia at the Battle of Manzikert, establishing the Seljuk Empire. To escape death or servitude at the hands of those who had assassinated his relative, Gagik II of Armenia, King of Ani, an Armenian named Ruben I, Prince of Armenia, went with some of his countrymen into the gorges of the Taurus Mountains and then into Tarsus of Cilicia. The Byzantine governor of the palace gave them shelter where the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia was eventually established on 6 January 1198 under Leo I, King of Armenia, a descendant of Prince Ruben.
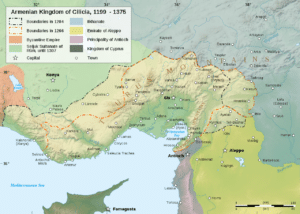
Cilicia was a strong ally of the European Crusaders, and saw itself as a bastion of Christendom in the East. Cilicia’s significance in Armenian history and statehood is also attested by the transfer of the seat of the Catholicos of the Armenian Apostolic Church, the spiritual leader of the Armenian people, to the region.
The Seljuk Empire soon started to collapse. In the early 12th century, Armenian princes of the Zakarid family drove out the Seljuk Turks and established a semi-independent principality in northern and eastern Armenia known as Zakarid Armenia, which lasted under the patronage of the Georgian Kingdom. The Orbelian Dynasty shared control with the Zakarids in various parts of the country, especially in Syunik and Vayots Dzor, while the House of Hasan-Jalalyan controlled provinces of Artsakh and Utik as the Kingdom of Artsakh.
Early Modern Era:
During the 1230s, the Mongol Empire conquered Zakarid Armenia and then the remainder of Armenia. The Mongolian invasions were soon followed by those of other Central Asian tribes, such as the Kara Koyunlu, Timurid dynasty and Ağ Qoyunlu, which continued from the 13th century until the 15th century. After incessant invasions, each bringing destruction to the country, with time Armenia became weakened.
In the 16th century, the Ottoman Empire and the Safavid dynasty of Iran divided Armenia. From the early 16th century, both Western Armenia and Eastern Armenia fell to the Safavid Empire. Owing to the century long Turco-Iranian geopolitical rivalry that would last in Western Asia, significant parts of the region were frequently fought over between the two rivalling empires. From the mid 16th century with the Peace of Amasya, and decisively from the first half of the 17th century with the Treaty of Zuhab until the first half of the 19th century, Eastern Armenia was ruled by the successive Safavid, Afsharid and Qajar empires, while Western Armenia remained under Ottoman rule.
From 1604, Abbas I of Iran implemented a “scorched earth” policy in the region to protect his north-western frontier against any invading Ottoman forces, a policy that involved a forced resettlement of masses of Armenians outside of their homelands.
In the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay, following the Russo-Persian War (1804–13) and the Russo-Persian War (1826–28), respectively, the Qajar dynasty of Iran was forced to irrevocably cede Eastern Armenia, consisting of the Erivan and Karabakh Khanates, to Imperial Russia.
