The PUP won a landslide victory in the 1998 national elections, and PUP leader Said Musa was sworn in as prime minister. In the 2003 elections the PUP maintained its majority, and Musa continued as prime minister. He pledged to improve conditions in the underdeveloped and largely inaccessible southern part of Belize.
In 2005, Belize was the site of unrest caused by discontent with the PUP government, including tax increases in the national budget. On 8 February 2008, Dean Barrow was sworn in as prime minister after his UDP won a landslide victory in general elections. Barrow and the UDP were re-elected in 2012 with a considerably smaller majority. Barrow led the UDP to a third consecutive general election victory in November 2015, increasing the party’s number of seats from 17 to 19. However he stated the election would be his last as party leader and preparations are under way for the party to elect his successor.
Geography:
Belize is on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America. It shares a border on the north with the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, on the west with the Guatemalan department of Petén, and on the south with the Guatemalan department of Izabal. To the east in the Caribbean Sea, the second-longest barrier reef in the world flanks much of the 240 miles of predominantly marshy coastline.

The area of the country totals 8,865 square miles, an area slightly larger than El Salvador, Israel, New Jersey or Wales.
The undulating courses of two rivers, the Hondo and the Sarstoon River, define much of the course of the country’s northern and southern boundaries. The western border follows no natural features and runs north-south through lowland forest and highland plateau.
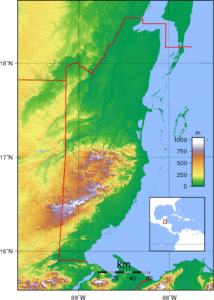
The north of Belize consists mostly of flat, swampy coastal plains, in places heavily forested. The flora is highly diverse considering the small geographical area. The south contains the low mountain range of the Maya Mountains. The highest point in Belize is Doyle’s Delight at 3,688 feet.
Economy:
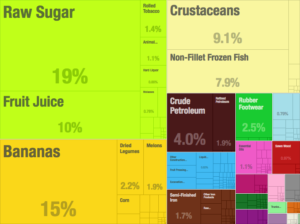
Belize has a small, mostly private enterprise economy that is based primarily on agriculture, agro-based industry, and merchandising, with tourism and construction recently assuming greater importance. The country is also a producer of industrial minerals, crude oil, and petroleum. As of 2017, oil production was 2,000 bbl/d. In agriculture, sugar, like in colonial times, remains the chief crop, accounting for nearly half of exports, while the banana industry is the largest employer.
The tourist and construction sectors strengthened in early 1999. Infrastructure remains a major economic development challenge; Belize has the region’s most expensive electricity. Trade is important and the major trading partners are the United States, Mexico, the European Union, and Central America.
A combination of natural factors—climate, the Belize Barrier Reef, over 450 offshore Cays (islands), excellent fishing, safe waters for boating, scuba diving, snorkelling and freediving, numerous rivers for rafting, and kayaking, various jungle and wildlife reserves of fauna and flora, for hiking, bird watching, and helicopter touring, as well as many Maya sites—support the thriving tourism and ecotourism industry. It also has the largest cave system in Central America.
