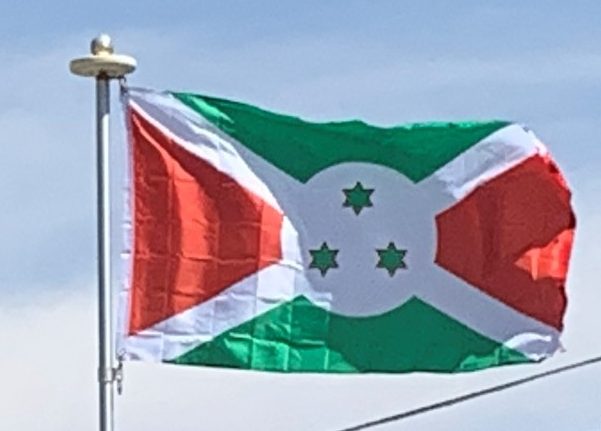
Introduction:
Burundi, officially the Republic of Burundi, is a landlocked country amid the African Great Lakes region where East and Central Africa converge. It is bordered by Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and southeast, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west; Lake Tanganyika lies along its southwestern border. The capital is Gitega, having moved from Bujumbura in February 2019.
The Twa, Hutu and Tutsi peoples have lived in Burundi for at least 500 years. For more than 200 of those years, Burundi was an independent kingdom, until the beginning of the 20th century, when Germany colonized the region. After the First World War and Germany’s defeat, it ceded the territory to Belgium. Both Germans and Belgians ruled Burundi and Rwanda as a European colony known as Ruanda-Urundi. Despite common misconceptions, Burundi and Rwanda had never been under common rule until the time of European colonization.
Burundi gained independence in 1962 and initially had a monarchy, but a series of assassinations, coups and a general climate of regional instability culminated in the establishment of a republic and one-party state in 1966. Bouts of ethnic cleansing and ultimately two civil wars and genocides during the 1970s and again in the 1990s left the country undeveloped and its population as one of the world’s poorest. The presidents of Rwanda and Burundi, both Hutus, died together when their aeroplane was shot down in April 1994. 2015 witnessed large-scale political strife as President Pierre Nkurunziza opted to run for a third term in office, a coup attempt failed and the country’s parliamentary and presidential elections were broadly criticized by members of the international community.
History:
Kingdom of Burundi:
The first evidence of the Burundian state dates back to the late 16th century where it emerged on the eastern foothills. Over the following centuries it expanded, annexing smaller neighbours. The Kingdom of Burundi, or Urundi, in the Great Lakes region was a polity ruled by a traditional monarch with several princes beneath him; succession struggles were common. The king, known as the mwami headed a princely aristocracy which owned most of the land and required a tribute, or tax, from local farmers (mainly Hutu) and herders (mainly Tutsi). The Kingdom of Burundi was characterized by a hierarchical political authority and tributary economic exchange.
In the mid-18th century, the Tutsi royalty consolidated authority over land, production, and distribution with the development of the ubugabire—a patron-client relationship in which the populace received royal protection in exchange for tribute and land tenure. By this time, the royal court was made up of the Tutsi-Banyaruguru, they had higher social status than other pastoralists such as the Tutsi-Hima. In the lower levels of this society were generally Hutu people, and at the very bottom of the pyramid were the Twa. The system had some fluidity however, some Hutu people belonged to the nobility and in this way also had a say in the functioning of the state.
