At independence in 1960, DRC was the second-most industrialized country in Africa after South Africa; it boasted a thriving mining sector and a relatively productive agriculture sector. The First and Second Congo Wars began in 1996. These conflicts have dramatically reduced national output and government revenue, increased external debt, and resulted in deaths of more than five million people from war and associated famine and disease. Malnutrition affects approximately two thirds of the country’s population.

Foreign businesses have curtailed operations due to uncertainty about the outcome of the conflict, lack of infrastructure, and the difficult operating environment. The war intensified the impact of such basic problems as an uncertain legal framework, corruption, inflation, and lack of openness in government economic policy and financial operations.
Conditions improved in late 2002, when a large portion of the invading foreign troops withdrew. A number of International Monetary Fund and World Bank missions met with the government to help it develop a coherent economic plan, and President Joseph Kabila began implementing reforms. Much economic activity still lies outside the GDP data. A United Nations Human Development Index report shows that the human development index of DRC is one of the worst the country has had in decades. Through 2011 the DRC had the lowest Human Development Index of the 187 ranked countries. It ranked lower than Niger, despite a higher margin of improvement than the latter country over 2010’s numbers.
A third of the DRC’s diamonds are believed to be smuggled out of the country, making it difficult to quantify diamond production levels. In 2002, tin was discovered in the east of the country, but to date has only been mined on a small scale. Smuggling of conflict minerals such as coltan and cassiterite, ores of tantalum and tin, respectively, helped to fuel the war in the Eastern Congo.
Transportation:
Ground transport in the Democratic Republic of Congo has always been difficult. The terrain and climate of the Congo Basin present serious barriers to road and rail construction, and the distances are enormous across this vast country. The DRC has more navigable rivers and moves more passengers and goods by boat and ferry than any other country in Africa, but air transport remains the only effective means of moving goods and people between many places within the country, especially in rural areas. Chronic economic mismanagement, political corruption and internal conflicts have led to long-term under-investment of infrastructure.
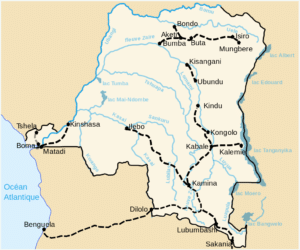
Rail transportation is provided by the Congo Railroad Company (Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer du Congo) and the Office National des Transports (Congo) (ONATRA) and the Office of the Uele Railways (Office des Chemins de fer des Ueles, CFU). Like much of the infrastructure in the Congo, the railways are poorly maintained, dirty, crowded and dangerous.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has fewer all-weather paved highways than any country of its population and size in Africa — a total of 2,250 km (1,400 mi), of which only 1,226 km (762 mi) is in good condition.
