A coalition of Rwandan and Ugandan armies invaded Zaire to overthrow the government of Mobutu, and ultimately to control the mineral resources of Zaire, launching the First Congo War. The coalition allied with some opposition figures, led by Laurent-Désiré Kabila, becoming the Alliance of Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Congo (AFDL). In 1997 Mobutu fled and Kabila marched into Kinshasa, named himself president, and reverted the name of the country to the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Kabila later requested that foreign military forces return to their own countries. He had concerns that the Rwandan officers running his army were plotting to give the presidency to a Tutsi who would report directly to Rwandan president, Paul Kagame. Rwandan troops retreated to Goma and launched a new Tutsi-led rebel military movement called the Rassemblement Congolais pour la Democratie (RCD) to fight Kabila, while Uganda instigated the creation of new rebel movement called the Movement for the Liberation of Congo (MLC), led by Congolese warlord Jean-Pierre Bemba. The two rebel movements, along with Rwandan and Ugandan troops, started the Second Congo War by attacking the DRC army in 1998. Angolan, Zimbabwean and Namibian militaries entered the hostilities on the side of the government.
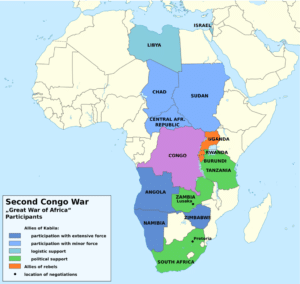
Kabila was assassinated in 2001. His son Joseph Kabila succeeded him and called for multilateral peace-talks. UN peacekeepers, MONUC, now known as MONUSCO, arrived in April 2001. In 2002 and 2003 Bemba intervened in the Central African Republic on behalf of its former president, Ange-Félix Patassé. Talks led to a peace accord under which Kabila would share power with former rebels. By June 2003 all foreign armies except those of Rwanda had pulled out of Congo. A transitional government was set up until after the election. A constitution was approved by voters, and on 30 July 2006 DRC held its first multi-party elections. An election-result dispute between Kabila and Jean-Pierre Bemba turned into an all-out battle between their supporters in the streets of Kinshasa. MONUC took control of the city. A new election took place in October 2006, which Kabila won, and on December 2006 he was sworn in as President.
Kivu Conflict:
Laurent Nkunda, a member of RCD-Goma, an RCD branch integrated to the army, defected along with troops loyal to him and formed the National Congress for the Defence of the People (CNDP), which began an armed rebellion against the government, starting the Kivu conflict. They were believed to be again backed by Rwanda as a way to tackle the Hutu group, Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR). In March 2009, after a deal between the DRC and Rwanda, Rwandan troops entered the DRC and arrested Nkunda and were allowed to pursue FDLR militants. The CNDP signed a peace treaty with the government in which it agreed to become a political party and to have its soldiers integrated into the national army in exchange for the release of its imprisoned members. In 2012 Bosco Ntaganda, the leader of the CNDP, and troops loyal to him, mutinied and formed the rebel military March 23 Movement, claiming the government violated the treaty.
