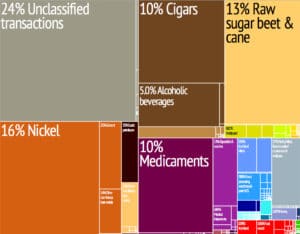
Cuba’s major exports are sugar, nickel, tobacco, fish, medical products, citrus fruits, and coffee; imports include food, fuel, clothing, and machinery. Cuba presently holds debt in an amount estimated at $13 billion, approximately 38% of GDP.
In May 2019, Cuba imposed rationing of staples such as chicken, eggs, rice, beans, soap and other basics. (Some two-thirds of food in the country is imported.) A spokesperson blamed the increased U.S. trade embargo although economists believe that an equally important problem is the massive decline of aid from Venezuela and the failure of Cuba’s state-run oil company which had subsidized fuel costs.
Tourism was initially restricted to enclave resorts where tourists would be segregated from Cuban society, referred to as “enclave tourism” and “tourism apartheid”. Contact between foreign visitors and ordinary Cubans were de facto illegal between 1992 and 1997. The rapid growth of tourism during the Special Period had widespread social and economic repercussions in Cuba, and led to speculation about the emergence of a two-tier economy.
Cuba has tripled its market share of Caribbean tourism in the last decade as a result of significant investment in tourism infrastructure, this growth rate is predicted to continue. 1.9 million tourists visited Cuba in 2003, predominantly from Canada and the European Union, generating revenue of US$2.1 billion. Cuba recorded 2,688,000 international tourists in 2011, the third-highest figure in the Caribbean (behind the Dominican Republic and Puerto Rico).

The medical tourism sector caters to thousands of European, Latin American, Canadian, and American consumers every year.
Geography:
Cuba is an archipelago of islands located in the northern Caribbean Sea at the confluence with the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. The United States lies 150 kilometers (93 miles) across the Straits of Florida to the north and northwest (to the closest tip of Key West, Florida), and the Bahamas 21 km (13 mi) to the north. Mexico lies 210 kilometers (130 miles) across the Yucatán Channel to the west (to the closest tip of Cabo Catoche in the State of Quintana Roo).
Haiti is 77 km (48 mi) to the east, Jamaica (140 km/87 mi) and the Cayman Islands to the south. Cuba is the principal island, surrounded by four smaller groups of islands: the Colorados Archipelago on the northwestern coast, the Sabana-Camagüey Archipelago on the north-central Atlantic coast, the Jardines de la Reina on the south-central coast and the Canarreos Archipelago on the southwestern coast.
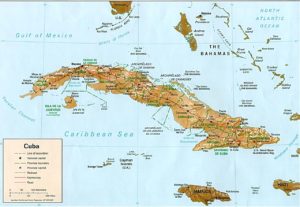
The main island, named Cuba, is 1,250 km (780 mi) long, constituting most of the nation’s land area (104,556 km2 (40,369 sq mi)) and is the largest island in the Caribbean and 17th-largest island in the world by land area. The main island consists mostly of flat to rolling plains apart from the Sierra Maestra mountains in the southeast, whose highest point is Pico Turquino (1,974 m (6,476 ft)).

