The Czech Republic is a developed country with an advanced, high income social market economy. It is a welfare state with a European social model, universal health care, and tuition-free university education. It ranks 13th in the UN inequality-adjusted human development and 14th in the World Bank Human Capital Index ahead of countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom and France. It ranks as the eleventh safest and most peaceful country and performs strongly in democratic governance. The Czech Republic joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union (EU) in 2004. It is also a member of the OECD, the United Nations, the OSCE, and the Council of Europe.
Etymology:
The traditional English name “Bohemia” derives from Latin “Boiohaemum”, which means “home of the Boii“. The current English name comes from the Polish ethnonym associated with the area, which ultimately comes from the Czech word Čech. The name comes from the Slavic tribe (Czech: Češi, Čechové) and, according to legend, their leader Čech, who brought them to Bohemia, to settle on Říp Mountain. The etymology of the word Čech can be traced back to the Proto-Slavic root *čel-, meaning “member of the people; kinsman”, thus making it cognate to the Czech word člověk (a person).
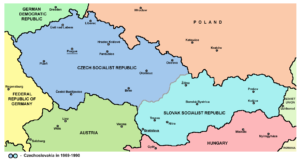
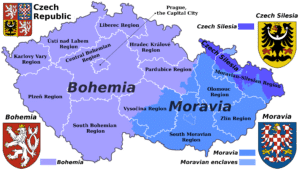
The country has been traditionally divided into three lands, namely Bohemia (Čechy) in the west, Moravia (Morava) in the east, and Czech Silesia (Slezsko; the smaller, south-eastern part of historical Silesia, most of which is located within modern Poland) in the northeast.
Known as the lands of the Bohemian Crown since the 14th century, a number of other names for the country have been used, including Czech/Bohemian lands, Bohemian Crown, Czechia and the lands of the Crown of Saint Wenceslas. When the country regained its independence after the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian empire in 1918, the new name of Czechoslovakia was coined to reflect the union of the Czech and Slovak nations within the one country.
After Czechoslovakia dissolved in 1992, the new Czech state lacked a common English short name. The Czech Ministry of Foreign Affairs recommended the English name Czechia in 1993, and the Czech government approved Czechia as the official short name in 2016.
History:
Prehistory:
Archaeologists have found evidence of prehistoric human settlements in the area, dating back to the Paleolithic era. The Venus of Dolní Věstonice, dated to 29,000–25,000 BCE, together with a few others from nearby locations, is the oldest known ceramic artifact in the world.

In the classical era, as a result of the 3rd century BC Celtic migrations, Bohemia became associated with the Boii. The Boii founded a city on the site of modern Prague; some of its ancient ruins are now a tourist attraction. According to a 2000 study by Semino, 35.6% of Czech males have y-chromosome haplogroup R1b, which is common among Celts but rare among Slavs. Some modern Czechs claim that the people are as much descendants of the Boii as they are from the later Slavic invaders (as well as the historical Germanic peoples of Czech lands).
