Introduction:
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 28 member states that are located primarily in Europe. It has an area of 4,475,757 km2 and an estimated population of about 513 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardized system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market, enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development. For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished. A monetary union was established in 1999 and came into full force in 2002 and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.
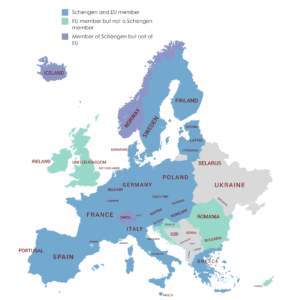
The EU and European citizenship were established when the Maastricht Treaty came into force in 1993. The EU traces its origins to the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) and the European Economic Community (EEC), established, respectively, by the 1951 Treaty of Paris and 1957 Treaty of Rome. The original members of what came to be known as the European Communities were the Inner Six: Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany. The Communities and its successors have grown in size by the accession of new member states and in power by the addition of policy areas to its remit. The latest major amendment to the constitutional basis of the EU, the Treaty of Lisbon, came into force in 2009. While no member state has left the EU or its antecedent organisations, the United Kingdom signified the intention to leave after a membership referendum in June 2016 and is negotiating its withdrawal on 29 March 2019.
Covering 7.3% of the world population, the EU in 2017 generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of 19.670 trillion US dollars, constituting approximately 24.6% of global nominal GDP.Additionally, all 28 EU countries have a very high Human Development Index, according to the United Nations Development Programme. In 2012, the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. Through the Common Foreign and Security Policy, the EU has developed a role in external relations and defense. The union maintains permanent diplomatic missions throughout the world and represents itself at the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, the G7 and the G20. Because of its global influence, the European Union has been described as an emerging superpower.
History:
Europe in the Early Middle Ages to the Middle of the 20th Century:
During the centuries following the fall of Rome in 476, several European States viewed themselves as translatio imperii of the defunct Roman Empire: the Frankish Empire (481–843) and the Holy Roman Empire (962–1806) were thereby attempts to resurrect Rome in the West.
This political philosophy of a supra-national rule over the continent, similar to the example of the ancient Roman Empire, resulted in the early Middle Ages in the concept of a renovatio imperii (“restoration of the empire), either in the forms of the Reichsidee (“imperial idea”) or the religiously inspired Imperium Christianum (“christian empire”). Medieval Christendom and the political power of the Papacy are often cited as conducive to European integration and unity.
