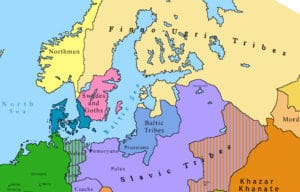
The 12th and 13th centuries were a violent time in the northern Baltic Sea. The Livonian Crusade was ongoing and the Finnish tribes such as the Tavastians and Karelians were in frequent conflicts with Novgorod and with each other. Also, during the 12th and 13th centuries several crusades from the Catholic realms of the Baltic Sea area were made against the Finnish tribes. According to historical sources, Danes waged two crusades on Finland, in 1191 and in 1202, and Swedes, possibly the so-called second crusade to Finland, in 1249 against Tavastians and the third crusade to Finland in 1293 against the Karelians. The so-called first crusade to Finland, possibly in 1155, is most likely an unreal event. Also, it is possible that Germans made violent conversion of Finnish pagans in the 13th century. According to a papal letter from 1241, the king of Norway was also fighting against “nearby pagans” at that time.
Swedish Era:
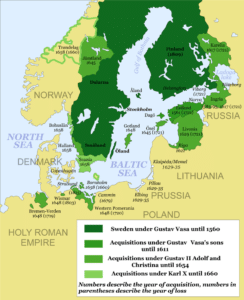
As a result of the crusades and the colonization of some Finnish coastal areas with Christian Swedish population during the Middle Ages, Finland gradually became part of the kingdom of Sweden and the sphere of influence of the Catholic Church. Due to the Swedish conquest, the Finnish upper class lost its position and lands to the new Swedish and German nobility and to the Catholic Church. In Sweden even in the 17th and 18th centuries, it was clear that Finland was a conquered country and its inhabitants could be treated arbitrarily. Swedish kings visited Finland rarely and in Swedish contemporary texts Finns were portrayed to be primitive and their language inferior.
Swedish became the dominant language of the nobility, administration, and education; Finnish was chiefly a language for the peasantry, clergy, and local courts in predominantly Finnish-speaking areas. During the Protestant Reformation, the Finns gradually converted to Lutheranism.
In the 16th century, Mikael Agricola published the first written works in Finnish. The first university in Finland, the Royal Academy of Turku, was established in 1640. Finland suffered a severe famine in 1696–1697, during which about one third of the Finnish population died, and a devastating plague a few years later.

In the 18th century, wars between Sweden and Russia twice led to the occupation of Finland by Russian forces, times known to the Finns as the Greater Wrath (1714–1721) and the Lesser Wrath (1742–1743). It is estimated that almost an entire generation of young men was lost during the Great Wrath, due mainly to the destruction of homes and farms, and to the burning of Helsinki. By this time Finland was the predominant term for the whole area from the Gulf of Bothnia to the Russian border.
Two Russo-Swedish wars in twenty-five years served as reminders to the Finnish people of the precarious position between Sweden and Russia. An increasingly vocal elite in Finland soon determined that Finnish ties with Sweden were becoming too costly, and following Russo-Swedish War (1788–1790), the Finnish elite’s desire to break with Sweden only heightened.
