Metropolitan France covers 551,500 square kilometres (212,935 sq mi), the largest among European Union members. France’s total land area, with its overseas departments and territories (excluding Adélie Land), is 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi), 0.45% of the total land area on Earth. France possesses a wide variety of landscapes, from coastal plains in the north and west to mountain ranges of the Alps in the southeast, the Massif Central in the south central and Pyrenees in the southwest.

Due to its numerous overseas departments and territories scattered across the planet, France possesses the second-largest Exclusive economic zone (EEZ) in the world, covering 11,035,000 km2 (4,260,000 mi2), just behind the EEZ of the United States.
Economy:
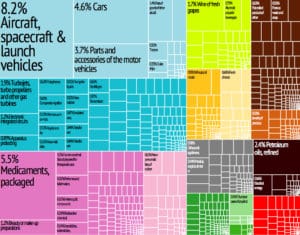
France has a mixed economy that combines extensive private enterprise with substantial state enterprise and government intervention. The government retains considerable influence over key segments of infrastructure sectors, with majority ownership of railway, electricity, aircraft, nuclear power and telecommunications. It has been relaxing its control over these sectors since the early 1990s. The government is slowly corporatizing the state sector and selling off holdings in France Télécom, Air France, as well as in the insurance, banking, and defense industries. France has an important aerospace industry led by the European consortium Airbus, and has its own national spaceport, the Centre Spatial Guyanais.

As of 2016, the World Factbook ranked France seventh largest exporter. In 2008, France was the third largest recipient of foreign direct investment among OECD countries at $118 billion, ranking behind Luxembourg (where foreign direct investment was essentially monetary transfers to banks located there) and the United States ($316 billion). In the same year, French companies invested $220 billion outside France, ranking France as the second largest outward direct investor in the OECD, behind the United States ($311 billion), and ahead of the UK ($111 billion), Japan ($128 billion) and Germany ($157 billion).
Financial services, banking and the insurance sector are an important part of the economy. Three largest financial institutions cooperatively owned by their customers are located in France. The Paris stock exchange is an old institution, created by Louis XV in 1724. In 2000, the stock exchanges of Paris, Amsterdam and Brussels merged into Euronext. In 2007, Euronext merged with the New York stock exchange to form NYSE Euronext, the world’s largest stock exchange. Euronext Paris, the French branch of the NYSE Euronext group is Europe’s 2nd largest stock exchange market, behind the London Stock Exchange.
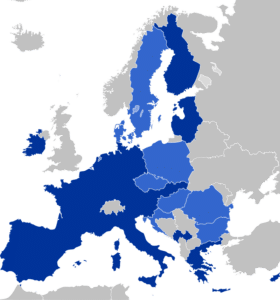
France is a member of the Eurozone (around 330 million consumers) which is part of the European Single Market (more than 500 million consumers). Several domestic commercial policies are determined by agreements among European Union (EU) members and by EU legislation. France introduced the common European currency, the Euro in 2002.
French companies have maintained key positions in the insurance and banking industries: AXA is the world’s largest insurance company. The leading French banks are BNP Paribas and the Crédit Agricole, ranking as the world’s first and sixth largest banks in 2010 (by assets), while the Société Générale group was ranked the world’s eighth largest in 2009.
