Introduction:
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country located along the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean, in the subregion of West Africa. Spanning a land mass of 238,535 km2 (92,099 sq mi), Ghana is bordered by the Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, Togo in the east, and the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean in the south. Ghana means “Warrior King” in the Soninke language.
The first permanent state in the territory of present-day Ghana dates back to the 11th century. Numerous kingdoms and empires emerged over the centuries, of which the most powerful was the Kingdom of Dagbon and the Kingdom of Ashanti. Beginning in the 15th century, the Portuguese Empire, followed by numerous other European powers, contested the area for trading rights, until the British ultimately established control of the coast by the late 19th century. Following over a century of native resistance, what are now Ghana’s borders follow the lines of what were four separate British colonial territories: Gold Coast, Ashanti, the Northern Territories and British Togoland. Those were unified as an independent dominion within the British Commonwealth on 6 March 1957.
Ghana’s population of approximately 30 million spans a variety of ethnic, linguistic and religious groups. According to the 2010 census, 71.2% of the population was Christian, 17.6% was Muslim, and 5.2% practised traditional faiths. Its diverse geography and ecology ranges from coastal savannas to tropical rain forests.
Ghana is a unitary constitutional democracy led by a president who is both head of state and head of the government. Ghana’s growing economic prosperity and democratic political system have made it a regional power in West Africa. It is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, the African Union, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), Group of 24 (G24) and the Commonwealth of Nations.
History:
Medieval Kingdoms:
Ghana was already recognized as one of the great kingdoms in Bilad el-Sudan by the ninth century.
Ghana was inhabited in the Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery by a number of ancient predominantly Akan kingdoms in the Southern and Central territories. This included the Ashanti Empire, the Akwamu, the Bonoman, the Denkyira, and the Mankessim Kingdom.
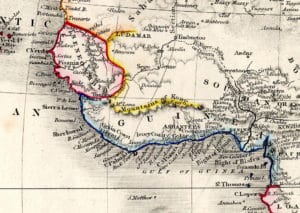
Although the area of present-day Ghana in West Africa has experienced many population movements, the Akans were firmly settled by the 5th century CE. By the early 11th century, the Akans were firmly established in the Akan state called Bonoman, for which the Brong-Ahafo Region is named.
From the 13th century, Akans emerged from what is believed to have been the Bonoman area, to create several Akan states of Ghana, mainly based on gold trading. These states included Bonoman (Brong-Ahafo Region), Ashanti (Ashanti Region), Denkyira (Western North region), Mankessim Kingdom (Central region), and Akwamu (Eastern region). By the 19th century, the territory of the southern part of Ghana was included in the Kingdom of Ashanti, one of the most influential states in sub-Saharan Africa prior to the onset of colonialism.
