There are several small islands off Jamaica’s coast, most notably those in Portland Bight such as Pigeon Island, Salt Island, Dolphin Island, Long Island, Great Goat Island and Little Goat Island, and also Lime Cay located further east. Much further out – some 50–80 km off the south coast – lie the very small Morant Cays and Pedro Cays.
Economy:
Jamaica is a mixed economy with both state enterprises and private sector businesses. Major sectors of the Jamaican economy include agriculture, mining, manufacturing, tourism, petroleum refining, financial and insurance services. Tourism and mining are the leading earners of foreign exchange.
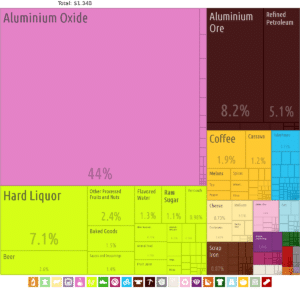
Half the Jamaican economy relies on services, with half of its income coming from services such as tourism. An estimated 4.3 million foreign tourists visit Jamaica every year. According to the World Bank, Jamaica is an upper-middle income country that, like its Caribbean neighbors, is vulnerable to the effects of climate change, flooding, and hurricanes. In 2018, Jamaica represented the CARICOM Caribbean Community at the G20 and the G7 annual meetings. In 2019 Jamaica reported its lowest unemployment rate in 50 years.
Transportation:
The transport infrastructure in Jamaica consists of roadways, railways and air transport, with roadways forming the backbone of the island’s internal transport system.[71]
The Jamaican road network consists of almost 21,000 kilometres (13,000 mi) of roads, of which over 15,000 kilometres (9,300 mi) is paved. The Jamaican Government has, since the late 1990s and in cooperation with private investors, embarked on a campaign of infrastructural improvement projects, one of which includes the creation of a system of freeways, the first such access-controlled roadways of their kind on the island, connecting the main population centres of the island. This project has so far seen the completion of 33 kilometres (21 mi) of freeway.
Railways in Jamaica no longer enjoy the prominent position they once did, having been largely replaced by roadways as the primary means of transport. Of the 272 kilometres (169 mi) of railway found in Jamaica, only 57 kilometres (35 mi) remain in operation, currently used to transport bauxite. On 13 April 2011, a limited passenger service was resumed between May Pen, Spanish Town and Linstead.

There are three international airports in Jamaica with modern terminals, long runways, and the navigational equipment required to accommodate the large jet aircraft used in modern air travel: Norman Manley International Airport in Kingston; Ian Fleming International Airport in Boscobel, Saint Mary Parish; and the island’s largest and busiest airport, Sir Donald Sangster International Airport in the resort city of Montego Bay. Manley and Sangster International airports were home to the country’s national airline, Air Jamaica. In addition there are local commuter airports at Tinson Pen (Kingston), Port Antonio, and Negril, which cater to internal flights only. Many other small, rural centres are served by private airstrips on sugar estates or bauxite mines.
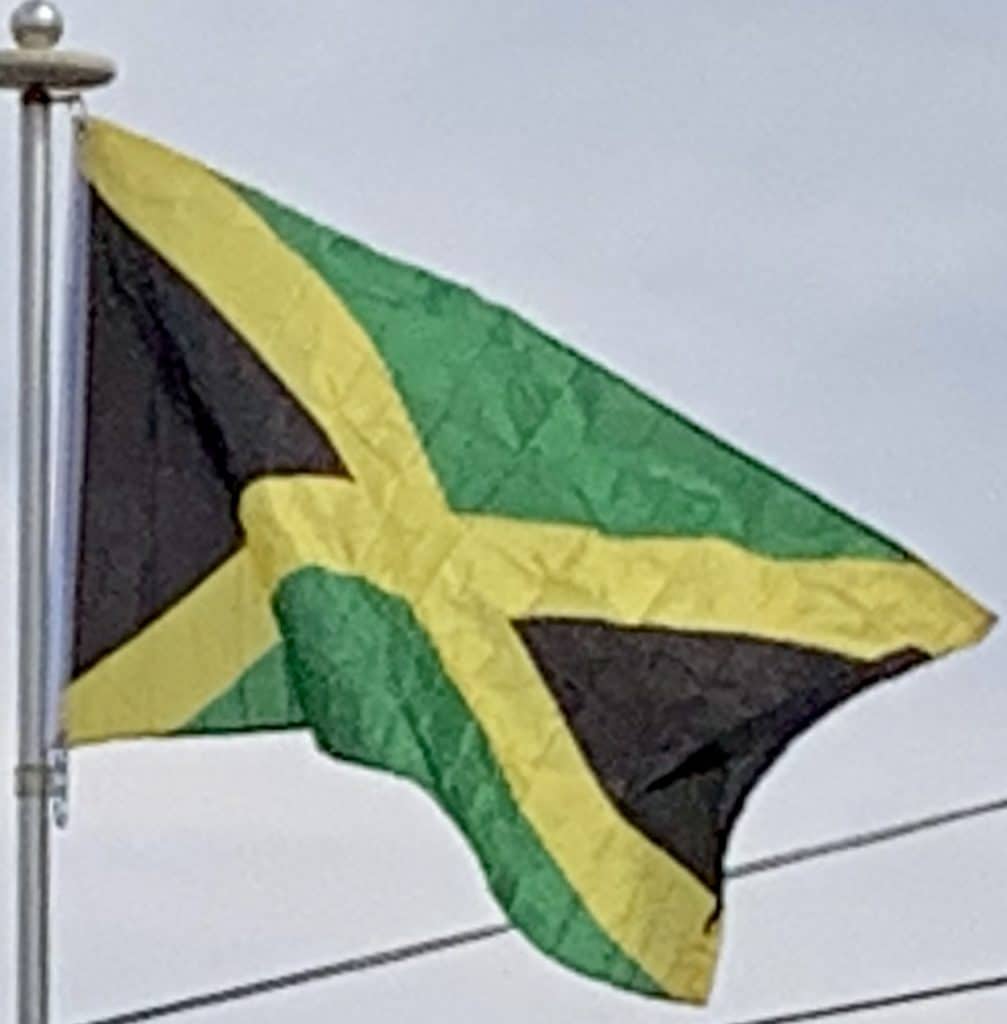
Flag of Jamaica:
The flag of Jamaica was adopted on 6 August 1962 (Jamaican Independence Day), the country having gained independence from the British-protected Federation of the West Indies. The flag consists of a gold saltire, which divides the flag into four sections: two of them green (top and bottom) and two black (hoist and fly). It is currently the only national flag that does not contain the colors red, white, or blue.
