The cause of the explosion was later determined to be 2,750 tonnes of ammonium nitrate that had been unsafely stored, and accidentally set on fire that Tuesday afternoon. Less than a week after the explosion, on August 10, 2020, Hassan Diab, the prime minister that had been designated less than a year before, addressed the nation and announced his resignation.
Geography:
Lebanon’s surface area is 10,452 square kilometres (4,036 sq mi) of which 10,230 square kilometres (3,950 sq mi) is land. Lebanon has a coastline and border of 225 kilometres (140 mi) on the Mediterranean Sea to the west, a 375 kilometres (233 mi) border shared with Syria to the north and east and a 79 kilometres (49 mi) long border with Israel to the south. The border with the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights is disputed by Lebanon in a small area called Shebaa Farms.
Lebanon is divided into four distinct physiographic regions: the coastal plain, the Lebanon mountain range, the Beqaa valley and the Anti-Lebanon mountains.
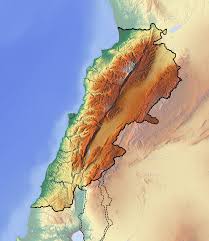
The narrow and discontinuous coastal plain stretches from the Syrian border in the north where it widens to form the Akkar plain to Ras al-Naqoura at the border with Israel in the south. The fertile coastal plain is formed of marine sediments and river deposited alluvium alternating with sandy bays and rocky beaches. The Lebanon mountains rise steeply parallel to the Mediterranean coast and form a ridge of limestone and sandstone that runs for most of the country’s length. The mountain range varies in width between 10 km (6 mi) and 56 km (35 mi); it is carved by narrow and deep gorges. The Lebanon mountains peak at 3,088 meters (10,131 ft) above sea level in Qurnat as Sawda’ in North Lebanon and gradually slope to the south before rising again to a height of 2,695 meters (8,842 ft) in Mount Sannine. The Beqaa valley sits between the Lebanon mountains in the west and the Anti-Lebanon range in the east; it is a part of the Great Rift Valley system. The valley is 180 km (112 mi) long and 10 to 26 km (6 to 16 mi) wide, its fertile soil is formed by alluvial deposits. The Anti-Lebanon range runs parallel to the Lebanon mountains, its highest peak is in Mount Hermon at 2,814 meters (9,232 ft).

The mountains of Lebanon are drained by seasonal torrents and rivers foremost of which is the 145 kilometers (90 mi) long Leontes that rises in the Beqaa Valley to the west of Baalbek and empties into the Mediterranean Sea north of Tyre. Lebanon has 16 rivers all of which are non navigable; 13 rivers originate from Mount Lebanon and run through the steep gorges and into the Mediterranean Sea, the other three arise in the Beqaa Valley.
Economy:
The Lebanese economy went through a significant expansion after the war of 2006, with growth averaging 9.1% between 2007 and 2010. After 2011 the local economy was affected by the Syrian civil war, growing by a yearly average of 1.7% on the 2011-2016 period and by 1.5% in 2017. In 2018, the size of the GDP was estimated to be $54.1 billion.
