In the mountainous sections of Malawi surrounding the Rift Valley, plateaus rise generally 914 to 1,219 meters (3,000 to 4,000 ft) above sea level, although some rise as high as 2,438 meters (8,000 ft) in the north. To the south of Lake Malawi lie the Shire Highlands, gently rolling land at approximately 914 meters (3,000 ft) above sea level. In this area, the Zomba and Mulanje mountain peaks rise to respective heights of 2,134 and 3,048 meters (7,000 and 10,000 ft).
Malawi’s capital is Lilongwe, and its commercial center is Blantyre with a population of over 500,000 people. Malawi has two sites listed on the UNESCO World Heritage List. Lake Malawi National Park was first listed in 1984 and the Chongoni Rock Art Area was listed in 2006.
Malawi’s climate is hot in the low-lying areas in the south of the country and temperate in the northern highlands. The altitude moderates what would otherwise be an equatorial climate. Between November and April the temperature is warm with equatorial rains and thunderstorms, with the storms reaching their peak severity in late March. After March, the rainfall rapidly diminishes and from May to September wet mists float from the highlands into the plateaus, with almost no rainfall during these months.
Economy:
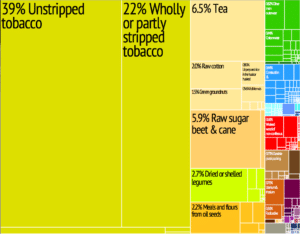
Malawi is among the world’s least developed countries. Around 85% of the population live in rural areas. The economy is based on agriculture, and more than one-third of GDP and 90% of export revenues come from this. In the past, the economy has been dependent on substantial economic aid from the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and other countries. Malawi was ranked the 119th safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 Euromoney Country Risk rankings.
In December 2000, the IMF stopped aid disbursements due to corruption concerns, and many individual donors followed suit, resulting in an almost 80% drop in Malawi’s development budget. However, in 2005, Malawi was the recipient of over US$575 million in aid. The Malawian government faces challenges in developing a market economy, improving environmental protection, dealing with the rapidly growing HIV/AIDS problem, improving the education system, and satisfying its foreign donors that it is working to become financially independent. Improved financial discipline had been seen since 2005 under the leadership of President Mutharika and Financial Minister Gondwe.
In addition, some setbacks have been experienced, and Malawi has lost some of its ability to pay for imports due to a general shortage of foreign exchange, as investment fell 23% in 2009. There are many investment barriers in Malawi, which the government has failed to address, including high service costs and poor infrastructure for power, water, and telecommunications.
Agriculture accounts for 35% of GDP, industry for 19% and services for the remaining 46%. Malawi has one of the lowest per capita incomes in the world, although economic growth was estimated at 9.7% in 2008 and strong growth is predicted by the International Monetary Fund for 2009. The poverty rate in Malawi is decreasing through the work of the government and supporting organizations, with people living under the poverty line decreasing from 54% in 1990 to 40% in 2006, and the percentage of “ultra-poor” decreasing from 24% in 1990 to 15% in 2007.
