The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) condemned the coup and demanded the reinstallation of President Keïta.
Geography:
Mali is a landlocked country in West Africa, located southwest of Algeria. Mali borders Algeria to the north-northeast, Niger to the east, Burkina Faso to the south-east, Ivory Coast to the south, Guinea to the south-west, and Senegal to the west and Mauritania to the north-west.
At 1,242,248 square kilometers (479,635 sq mi), Mali is the world’s 24th-largest country and is comparable in size to South Africa or Angola. Most of the country lies in the southern Sahara Desert, which produces an extremely hot, dust-laden Sudanian savanna zone. Mali is mostly flat, rising to rolling northern plains covered by sand. The Adrar des Ifoghas massif lies in the northeast.
Mali lies in the torrid zone and is among the hottest countries in the world. The thermal equator, which matches the hottest spots year-round on the planet based on the mean daily annual temperature, crosses the country. Most of Mali receives negligible rainfall and droughts are very frequent. Late April to early October is the rainy season in the southernmost area. During this time, flooding of the Niger River is common, creating the Inner Niger Delta. The vast northern desert part of Mali has a hot desert climate with long, extremely hot summers and scarce rainfall which decreases northwards. The central area has a hot semi-arid climate with very high temperatures year-round, a long, intense dry season and a brief, irregular rainy season. The southern areas have a tropical wet and dry climate. In review, Mali’s climate is tropical, with March to May being the hot, dry season. June to October is rainy, humid and mild. November to February is the cool, dry season.
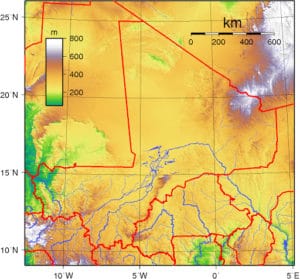
Mali has considerable natural resources, with gold, uranium, phosphates, kaolinite, salt and limestone being most widely exploited. Mali is estimated to have in excess of 17,400 tons of uranium. In 2012, a further uranium mineralized north zone was identified. Mali faces numerous environmental challenges, including desertification, deforestation, soil erosion, and inadequate supplies of potable water.
Economy:
The Central Bank of West African States handles the financial affairs of Mali and additional members of the Economic Community of West African States. Mali is considered one of the poorest countries in the world. The average worker’s annual salary is approximately US$1,500.
Mali underwent economic reform, beginning in 1988 by signing agreements with the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund. During 1988 to 1996, Mali’s government largely reformed public enterprises. Since the agreement, sixteen enterprises were privatized, 12 partially privatized, and 20 liquidated. In 2005, the Malian government conceded a railroad company to the Savage Corporation. Two major companies, Societé de Telecommunications du Mali (SOTELMA) and the Cotton Ginning Company (CMDT), were expected to be privatized in 2008.

