Between 1992 and 1995, Mali implemented an economic adjustment program that resulted in economic growth and a reduction in financial imbalances. The program increased social and economic conditions, and led to Mali joining the World Trade Organization on 31 May 1995.
Mali is a part of the “Franc Zone” (Zone Franc), which means that it uses the CFA franc. Mali is connected with the French government by agreement since 1962 (creation of BCEAO). Today all seven countries of BCEAO (including Mali) are connected to French Central Bank.
Mali’s key industry is agriculture. Cotton is the country’s largest crop export and is exported west throughout Senegal and Côte d’Ivoire. During 2002, 620,000 tons of cotton were produced in Mali but cotton prices declined significantly in 2003. In addition to cotton, Mali produces rice, millet, corn, vegetables, tobacco, and tree crops. Gold, livestock and agriculture amount to 80% of Mali’s exports.
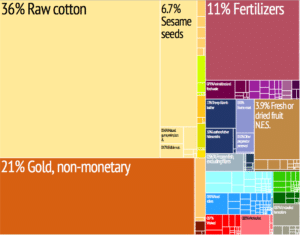
Eighty percent of Malian workers are employed in agriculture. 15% of Malian workers are employed in the service sector. Seasonal variations lead to regular temporary unemployment of agricultural workers.
In 1991, with the assistance of the International Development Association, Mali relaxed the enforcement of mining codes which led to renewed foreign interest and investment in the mining industry. Gold is mined in the southern region and Mali has the third highest gold production in Africa (after South Africa and Ghana).
The emergence of gold as Mali’s leading export product since 1999 has helped mitigate some of the negative impact of the cotton and Ivory Coast crises. Other natural resources include kaolin, salt, phosphate, and limestone.
Transportation:
Mali’s transportation infrastructure is regarded as poor, even by regional standards, and deficiencies have limited economic growth and development. Nevertheless, improvements have been noted in the early 2000s. Most of the transportation in Mali consists of cars, planes, and boats.
Mali has one railroad (the Dakar-Niger Railway), including 729 kilometers in Mali, which runs from the port of Koulikoro via Bamako to the border with Senegal and continues on to Dakar. The Bamako-Dakar line, which has been described as dilapidated, was owned by a joint company established by Mali and Senegal in 1995, with the eventual goal of privatization. In 2003 the two countries sold a 25-year concession to run the rail line to a Canadian company, which has pledged to upgrade equipment and infrastructure.
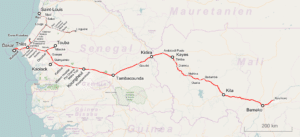
The Malian portion of the railroad carried an estimated 536,000 tons of freight and 778,000 passengers in 1999. The track is in poor condition, and the line is closed frequently during the rainy season. The line is potentially significant because it links landlocked Mali to the port of Dakar, increasingly of interest for Malian exports in the face of the disruption of access to Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, as a result of civil conflict in that country beginning in late 2002. In the early 2000s, there also were plans to construct a new rail line between Bamako and Kouroussa and Kankan in Guinea.
