Mexico’s ability to maintain its independence and establish a viable government was in question. Spain attempted to reconquer its former colony during the 1820s, but eventually recognized its independence. France attempted to recoup losses it claimed for its citizens during Mexico’s unrest and blockaded the Gulf Coast during the so-called Pastry War of 1838–39. Emerging as a national hero in defending Mexico was creole army general, Antonio López de Santa Anna, who had participated in the overthrow of the emperor, fought the Spanish invasion, and came to dominate the politics for the next 25 years, until his own overthrow in 1855.

Mexico also contended with indigenous groups which controlled territory that Mexico claimed in the north. The Comanche controlled a huge territory in the sparsely populated region of central and northern Texas. Wanting to stabilize and develop the frontier, the Mexican government encouraged Anglo-American immigration into present-day Texas. The region bordered the United States, and was territory controlled by Comanches. There were few settlers from central Mexico moving to this remote and hostile territory. Mexico by law was a Catholic country; the Anglo Americans were primarily Protestant English speakers from the southern United States. Some brought their black slaves, which after 1829 was contrary to Mexican law. Santa Anna sought to centralize government rule, suspending the constitution and promulgating the Seven Laws, which place power in his hands. When he suspended the 1824 Constitution, civil war spread across the country. Three new governments declared independence: the Republic of Texas, the Republic of the Rio Grande and the Republic of Yucatán.
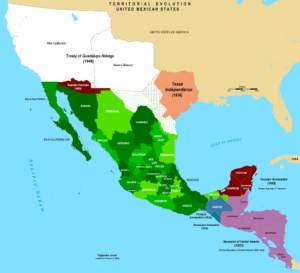
The largest blow to Mexico was the U.S. invasion of Mexico in 1846 in the Mexican American War. Mexico lost much of its sparsely populated northern territory, sealed in the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. Despite that disastrous loss, Conservative Santa Anna returned to the presidency yet again and then was ousted and exiled in the Liberal Revolution of Ayutla.
Liberal Reform, French Intervention, and Restored Republic (1855–1876):
The overthrow of Santa Anna and the establishment of a civilian government by Liberals allowed them to enact laws that they considered vital for Mexico’s economic development. It was a prelude to more civil wars and yet another foreign invasion. The Liberal Reform attempted to modernize Mexico’s economy and institutions along liberal principles. They promulgated a new Constitution of 1857, separating Church and State, stripping the Conservative institutions of the Church and the military of their special privileges (fueros); mandating the sale of Church-owned property and sale of indigenous community lands, and secularizing education. Conservatives revolted, touching off civil war between rival Liberal and Conservative governments (1858–61).
The Liberals defeated the Conservative army on the battlefield, but Conservatives sought another solution to gain power via foreign intervention by the French. Mexican conservatives asked Emperor Napoleon III to place a European monarch as head of state in Mexico. The French Army defeated the Mexican Army and placed Maximilian Hapsburg on the newly established throne of Mexico, supported by Mexican Conservatives and propped up by the French Army.
