Introduction:
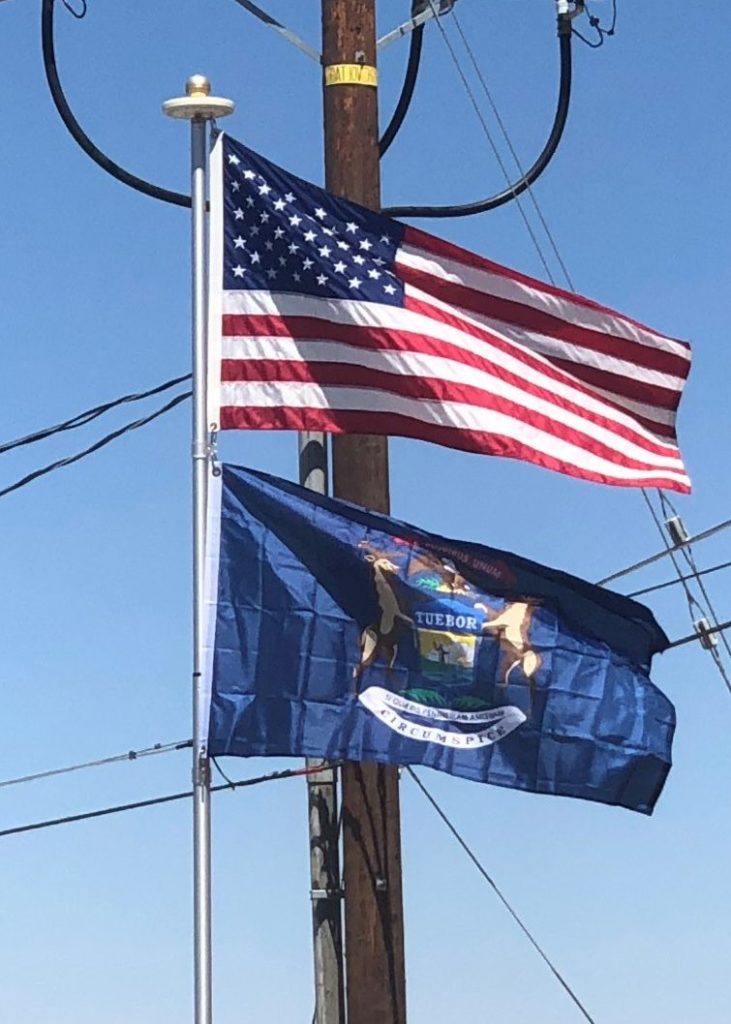
Michigan is a state in the Great Lakes and Midwestern regions of the United States.
The state’s name, Michigan, originates from the Ojibwe word mishigamaa, meaning “large water” or “large lake”. Michigan is the tenth most populous of the 50 United States, with the 11th most extensive total area, and is the largest state by total area east of the Mississippi River. Michigan has a population of about 10 million. Its capital is Lansing.

Metro Detroit is among the nation’s most populous and largest metropolitan economies.
Michigan is the only state to consist of two peninsulas. The Lower Peninsula, to which the name Michigan was originally applied, is often noted as shaped like a mitten. The Upper Peninsula, often called “the U.P., is separated from the Lower Peninsula by the Straits of Mackinac, a five-mile channel that joins Lake Huron to Lake Michigan. The Mackinac Bridge connects the peninsulas.

The state has the longest freshwater coastline of any political subdivision in the world, being bounded by four of the five Great Lakes, plus Lake Saint Clair. As a result, it is one of the leading U.S. states for recreational boating. Michigan also has 64,980 inland lakes and ponds. A person in the state is never more than six miles from a natural water source or more than 85 miles from a Great Lakes shoreline.
History:
Pre-European Contact:
When the first European explorers arrived, the most populous tribes were Algonquian peoples, which include the Anishinaabe groups of Ojibwe (referred to as “Chippewa” in the United States), Odaawaa/Odawa (Ottawa), and the Boodewaadamii/Bodéwadmi (Potawatomi). The three nations co-existed peacefully as part of a loose confederation called the Council of Three Fires. The Ojibwe, whose numbers are estimated to have been between 25,000 and 35,000, were the largest.

The Ojibwe were established in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula and northern and central Michigan, and also inhabited Ontario and southern Manitoba, Canada; and northern Wisconsin, and northern and north-central Minnesota. The Ottawa lived primarily south of the Straits of Mackinac in northern, western and southern Michigan, but also in southern Ontario, northern Ohio and eastern Wisconsin. The Potawatomi were in southern and western Michigan, in addition to northern and central Indiana, northern Illinois, southern Wisconsin, and southern Ontario. Other Algonquian tribes in Michigan, in the south and east, were the Mascouten, the Menominee, the Miami, the Sac (or Sauk), and the Fox. The Wyandot were an Iroquoian-speaking people in this area; they were historically known as the Huron by the French.
17th century:
French voyageurs and coureurs des bois explored and settled in Michigan in the 17th century. The first Europeans to reach what became Michigan were those of Étienne Brûlé‘s expedition in 1622. The first permanent European settlement was founded in 1668 on the site where Père Jacques Marquette established Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan as a base for Catholic missions.
