In the mid-to-late 9th century the Bamar people founded a small settlement at Bagan. It was one of several competing city-states until the late 10th century when it grew in authority and grandeur.
Pagan Kingdom:
Pagan gradually grew to absorb its surrounding states until the 1050s–1060s when Anawrahta founded the Pagan Kingdom, the first ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Pagan Empire and the Khmer Empire were two main powers in mainland Southeast Asia. The Burmese language and culture gradually became dominant in the upper Irrawaddy valley. Theravada Buddhism slowly began to spread to the village level. Repeated Mongol invasions in the late 13th century toppled the four-century-old kingdom in 1287.
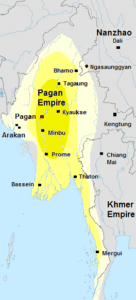
Pagan’s collapse was followed by 250 years of political fragmentation that lasted well into the 16th century. Like the Burmans four centuries earlier, Shan migrants who arrived with the Mongol invasions stayed behind. Several competing Shan States came to dominate the entire northwestern to eastern arc surrounding the Irrawaddy valley. The valley too was beset with petty states until the late 14th century when two sizeable powers, Ava Kingdom and Hanthawaddy Kingdom, emerged. In the west, a politically fragmented Arakan was under competing influences of its stronger neighbors until the Kingdom of Mrauk U unified the Arakan coastline for the first time in 1437. The kingdom was a protectorate of the Bengal Sultanate at different time periods.
In the 14th and 15th centuries, Ava fought wars of unification but could never quite reassemble the lost empire. Having held off Ava, the Mon-speaking Hanthawaddy entered its golden age, and Arakan went on to become a power in its own right for the next 350 years. In contrast, constant warfare left Ava greatly weakened, and it slowly disintegrated from 1481 onward. In 1527, the Confederation of Shan States conquered Ava and ruled Upper Myanmar until 1555.
Taungoo and Konbaung:
Political unification returned in the mid-16th century, through the efforts of Taungoo, a former vassal state of Ava.
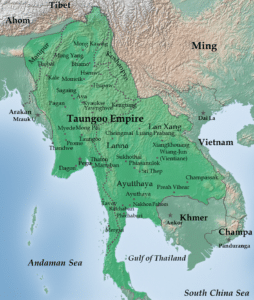
Taungoo’s young, ambitious King Tabinshwehti defeated the more powerful Hanthawaddy in the Toungoo–Hanthawaddy War. His successor Bayinnaung went on to conquer a vast swath of mainland Southeast Asia including the Shan states, Lan Na, Manipur, Mong Mao, the Ayutthaya Kingdom, Lan Xang and southern Arakan. However, the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia unraveled soon after Bayinnaung’s death in 1581, completely collapsing by 1599. Ayutthaya seized Tenasserim and Lan Na, and Portuguese mercenaries established Portuguese rule at Thanlyin (Syriam).
The dynasty regrouped and defeated the Portuguese in 1613 and Siam in 1614. It restored a smaller, more manageable kingdom, encompassing Lower Myanmar, Upper Myanmar, Shan states, Lan Na and upper Tenasserim. The restored Toungoo kings created a legal and political framework whose basic features continued well into the 19th century. The crown completely replaced the hereditary chieftainships with appointed governorships in the entire Irrawaddy valley and greatly reduced the hereditary rights of Shan chiefs. Its trade and secular administrative reforms built a prosperous economy for more than 80 years. From the 1720s onward, the kingdom was beset with repeated Meithei raids into Upper Myanmar and a nagging rebellion in Lan Na. In 1740, the Mon of Lower Myanmar founded the Restored Hanthawaddy Kingdom. Hanthawaddy forces sacked Ava in 1752, ending the 266-year-old Toungoo Dynasty.
