Nigeria is the United States’ largest trading partner in sub-Saharan Africa and supplies a fifth of its oil (11% of oil imports). It has the seventh-largest trade surplus with the U.S. of any country worldwide. Nigeria is the 50th-largest export market for U.S. goods and the 14th-largest exporter of goods to the U.S. The United States is the country’s largest foreign investor.

Economic development has been hindered by years of military rule, corruption, and mismanagement. The restoration of democracy and subsequent economic reforms have successfully put Nigeria back on track towards achieving its full economic potential. As of 2014 it is the largest economy in Africa, having overtaken South Africa. Next to petrodollars, the second-biggest source of foreign exchange earnings for Nigeria are remittances sent home by Nigerians living abroad.
Nigeria made history in April 2006 by becoming the first African country to completely pay off its debt (estimated $30 billion) owed to the Paris Club.
Nigeria is trying to reach the Sustainable Development Goal Number 1, which is to end poverty in all its forms by 2030.
As of 2010, about 30% of Nigerians are employed in agriculture. Major crops include beans, sesame, cashew nuts, cassava, cocoa beans, groundnuts, gum arabic, kolanut, maize (corn), melon, millet, palm kernels, palm oil, plantains, rice, rubber, sorghum, soybeans and yams. Cocoa is the leading non-oil foreign exchange earner. Rubber is the second-largest non-oil foreign exchange earner.
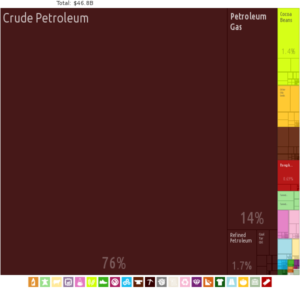
Nigeria is the 12th largest producer of petroleum in the world and the 8th largest exporter, and has the 10th largest proven reserves. Petroleum plays a large role in the Nigerian economy, accounting for 40% of GDP and 80% of Government earnings. However, agitation for better resource control in the Niger Delta, its main oil-producing region, has led to disruptions in oil production and prevents the country from exporting at 100% capacity.
In addition to its petroleum resources, Nigeria also has a wide array of underexploited mineral resources which include natural gas, coal, bauxite, tantalite, gold, tin, iron ore, limestone, niobium, lead and zinc. Despite huge deposits of these natural resources, the mining industry in Nigeria is still in its infancy.
Transportation:
Nigeria suffers from lack of adequate transportation infrastructure. As of 1999, its 194,394 kilometers of road networks are the main means of transportation. Of which 60,068 kilometres (37,325 mi) (including 1,194 km (742 mi) of expressways) are paved roads and as of 1998, 134,326 kilometers are unpaved roads of city, town and village roads.
The railways have undergone a massive revamping with projects such as the Lagos-Kano Standard Gauge Railway being completed connecting northern cities of Kano, Kaduna, Abuja, Ibadan and Lagos.
There are 54 airports in Nigeria; the principal airports are Murtala Muhammed International Airport in Lagos and Nnamdi Azikiwe International Airport in Abuja. Three other international airports are Mallam Aminu Kano International Airport in Kano, Akanu Ibiam International Airport in Enugu and Port Harcourt International Airport in Port Harcourt. As with other transportation facilities, the airports suffer from a poor reputation for safety and operational efficiency.
Flag of Nigeria:
The flag of Nigeria was designed in 1959 and first officially hoisted on 1 October 1960. The flag has three vertical bands of green, white, green. The two green stripes represent natural wealth, and the white represent peace and unity.
