In contrast to the Indian National Congress’s anti-British efforts, the Muslim League was a pro-British movement whose political program inherited the British values that would shape Pakistan’s future civil society. In events during World War I, British Intelligence foiled an anti-English conspiracy involving the nexus of Congress and the German Empire. The largely non-violent independence struggle led by the Indian Congress engaged millions of protesters in mass campaigns of civil disobedience in the 1920s and 1930s against the British Empire.
The Muslim League slowly rose to mass popularity in the 1930s amid fears of under-representation and neglect of British Muslims in politics. In his presidential address of 29 December 1930, Allama Iqbal called for “the amalgamation of North-West Muslim-majority Indian states” consisting of Punjab, North-West Frontier Province, Sind, and Baluchistan. The perceived neglect of Muslim interests by Congress led British provincial governments during the period of 1937–39 convinced Muhammad Ali Jinnah, the founder of Pakistan to espouse the two-nation theory and led the Muslim League to adopt the Lahore Resolution of 1940 presented by Sher-e-Bangla A.K. Fazlul Haque, popularly known as the Pakistan Resolution.

In World War II, Jinnah and British-educated founding fathers in the Muslim League supported the United Kingdom’s war efforts, countering opposition against it whilst working towards Sir Syed’s vision.
Pakistan Movement:
The 1946 elections resulted in the Muslim League winning 90 percent of the seats reserved for Muslims. Thus, the 1946 election was effectively a plebiscite in which the Indian Muslims were to vote on the creation of Pakistan, a plebiscite won by the Muslim League. This victory was assisted by the support given to the Muslim League by the support of the landowners of Sindh and Punjab. The Congress, which initially denied the Muslim League’s claim of being the sole representative of Indian Muslims, was now forced to recognize the fact. The British had no alternative except to take Jinnah’s views into account as he had emerged as the sole spokesperson of the entirety of British India’s Muslims. However, the British did not want colonial India to be partitioned, and in one last effort to prevent it, they devised the Cabinet Mission plan.
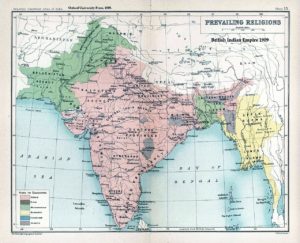
As the cabinet mission failed, the British government announced its intention to end the British Rule in 1946–47. Nationalists in British India—including Jawaharlal Nehru and Abul Kalam Azad of Congress, Jinnah of the All-India Muslim League, and Master Tara Singh representing the Sikhs—agreed to the proposed terms of transfer of power and independence in June 1947 with the Viceroy of India, Lord Mountbatten of Burma. As the United Kingdom agreed to the partitioning of India in 1947, the modern state of Pakistan was established on 14 August 1947 (27th of Ramadan in 1366 of the Islamic Calendar), amalgamating the Muslim-majority eastern and northwestern regions of British India. It comprised the provinces of Balochistan, East Bengal, the North-West Frontier Province, West Punjab, and Sindh.
