Rwanda is a country of few natural resources, and the economy is based mostly on subsistence agriculture by local farmers using simple tools. An estimated 90% of the working population farms, and agriculture constituted an estimated 32.5% of GDP in 2014. Farming techniques are basic, with small plots of land and steep slopes. Since the mid-1980s, farm sizes and food production have been decreasing, due in part to the resettlement of displaced people. Despite Rwanda’s fertile ecosystem, food production often does not keep pace with population growth, and food imports are required, but in recent years, with the growth of agriculture, the situation has improved.
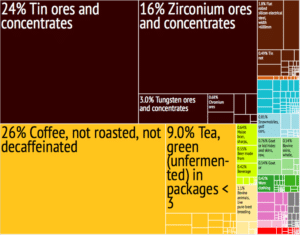
Subsistence crops grown in the country include matoke (green bananas), which occupy more than a third of the country’s farmland, potatoes, beans, sweet potatoes, cassava, wheat and maize. Coffee and tea are the major cash crops for export, with the high altitudes, steep slopes and volcanic soils providing favorable conditions. Reports have established that more than 400,000 Rwandans make their living from coffee plantation. Reliance on agricultural exports makes Rwanda vulnerable to shifts in their prices. Animals raised in Rwanda include cows, goats, sheep, pigs, chicken, and rabbits, with geographical variation in the numbers of each. Production systems are mostly traditional, although there are a few intensive dairy farms around Kigali. Shortages of land and water, insufficient and poor-quality feed, and regular disease epidemics with insufficient veterinary services are major constraints that restrict output. Fishing takes place on the country’s lakes, but stocks are very depleted, and live fish are being imported in an attempt to revive the industry.

The industrial sector is small, contributing 14.8% of GDP in 2014. Products manufactured include cement, agricultural products, small-scale beverages, soap, furniture, shoes, plastic goods, textiles and cigarettes. Rwanda’s mining industry is an important contributor, generating US$93 million in 2008. Minerals mined include cassiterite, wolframite, gold, and coltan, which is used in the manufacture of electronic and communication devices such as mobile phones.
Rwanda’s service sector suffered during the late-2000s recession as bank lending, foreign aid projects and investment were reduced. The sector rebounded in 2010, becoming the country’s largest sector by economic output and contributing 43.6% of the country’s GDP. Key tertiary contributors include banking and finance, wholesale and retail trade, hotels and restaurants, transport, storage, communication, insurance, real estate, business services and public administration including education and health. Tourism is one of the fastest-growing economic resources and became the country’s leading foreign exchange earner in 2007. In spite of the genocide’s legacy, the country is increasingly perceived internationally as a safe destination. The number of tourist arrivals in 2013 was 864,000 people, up from 504,000 in 2010.

Revenue from tourism was US$303 million in 2014, up from just US$62 million in 2000. The largest contributor to this revenue was mountain gorilla tracking, in the Volcanoes National Park; Rwanda is one of only three countries in which mountain gorillas can be visited safely; the gorillas attract thousands of visitors per year, who are prepared to pay high prices for permits. Other attractions include Nyungwe Forest, home to chimpanzees, Ruwenzori colobus and other primates, the resorts of Lake Kivu, and Akagera, a small savanna reserve in the east of the country.
Transportation:
The government has increased investment in the transport infrastructure of Rwanda since the 1994 genocide, with aid from the United States, European Union, Japan, and others. The transport system consists primarily of the road network, with paved roads between Kigali and most other major cities and towns in the country. Rwanda is linked by road to other countries in the East African Community, namely Uganda, Tanzania, Burundi and Kenya, as well as to the eastern Congolese cities of Goma and Bukavu; the country’s most important trade route is the road to the port of Mombasa via Kampala and Nairobi, which is known as the Northern Corridor.
