At the end of December 2011, Samoa changed its time zone offset from UTC−11 to UTC+13, effectively jumping forward by one day, omitting Friday, 30 December from the local calendar. This also had the effect of changing the shape of the International Date Line, moving it to the east of the territory. This change aimed to help the nation boost its economy in doing business with Australia and New Zealand. Before this change, Samoa was 21 hours behind Sydney, but the change means it is now three hours ahead. The previous time zone, implemented on 4 July 1892, operated in line with American traders based in California.
In June 2017, Parliament established an amendment to Article 1 of the Samoan Constitution, thereby making Christianity the state religion.

In May 2021, Fiame Naomi Mataʻafa is due to become Samoa’s first female prime minister. Mataʻafa’s FAST party narrowly won the election, ending the rule of long-term Prime Minister Tuilaepa Sailele Malielegaoi, although the constitutional crisis complicates this. On 24 May 2021, she was sworn in as the new prime minister.
Geography:
Samoa lies south of the equator, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand, in the Polynesian region of the Pacific Ocean. The total land area is 2,842 km2 (1,097 sq mi), consisting of the two large islands of Upolu and Savai’i (which together account for 99% of the total land area) and eight small islets.
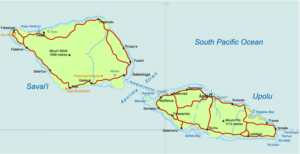
The main island of Upolu is home to nearly three-quarters of Samoa’s population, and to the capital city, Apia.
The Samoan islands result geologically from volcanism, originating with the Samoa hotspot, which probably results from a mantle plume. While all of the islands have volcanic origins, only Savai’i, the westernmost island in Samoa, remains volcanically active, with the most recent eruptions at Mt Matavanu (1905–1911), Mata o le Afi (1902) and Mauga Afi (1725).
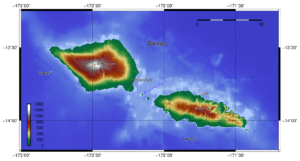
The highest point in Samoa is Mt Silisili, at 1858 m (6,096 ft). The Saleaula lava fields situated on the central north coast of Savai’i result from the Mt Matavanu eruptions, which left 50 km2 (20 sq mi) of solidified lava.
Economy:
The United Nations has classified Samoa as an economically developing country since 2014. As of 2017 Samoa’s gross domestic product in purchasing-power parity was estimated at $1.13 billion U.S. dollars, ranking the country 204th in the world. The services sector accounted for 66% of GDP, followed by industry and agriculture at 23.6% and 10.4% respectively.
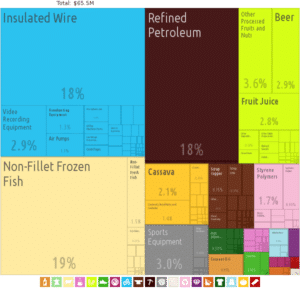
The Central Bank of Samoa issues and regulates Samoa’s currency, the Samoan tālā. The economy of Samoa has traditionally depended on agriculture and fishing at the local level. In modern times, development aid, private family remittances from overseas, and agricultural exports have become key factors in the nation’s economy. Agriculture employs two-thirds of the labor force and furnishes 90% of exports, featuring coconut cream, coconut oil, noni (juice of the nonu fruit, as it is known in Samoan), and copra.
