Upon Rastislav’s request, two brothers, Byzantine officials and missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius came in 863. Cyril developed the first Slavic alphabet and translated the Gospel into the Old Church Slavonic language. Rastislav was also preoccupied with the security and administration of his state. Numerous fortified castles built throughout the country are dated to his reign and some of them are also mentioned in connection with Rastislav by Frankish chronicles.
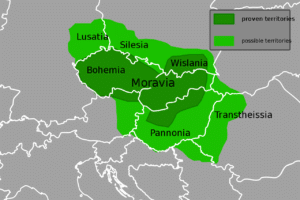
During Rastislav’s reign, the Principality of Nitra was given to his nephew Svätopluk as an appanage. The rebellious prince allied himself with the Franks and overthrew his uncle in 870. Similarly to his predecessor, Svätopluk I (871–894) assumed the title of the king (rex). During his reign, the Great Moravian Empire reached its greatest territorial extent, when not only present-day Moravia and Slovakia but also present-day northern and central Hungary, Lower Austria, Bohemia, Silesia, Lusatia, southern Poland and northern Serbia belonged to the empire, but the exact borders of his domains are still disputed by modern authors. Svatopluk also withstood attacks of the Magyar tribes and the Bulgarian Empire, although sometimes it was he who hired the Magyars when waging war against East Francia.
In 880, Pope John VIII set up an independent ecclesiastical province in Great Moravia with Archbishop Methodius as its head. He also named the German cleric Wiching the Bishop of Nitra.
Weakened by an internal conflict as well as by constant warfare with Eastern Francia, Great Moravia lost most of its peripheral territories.
In the meantime, the semi-nomadic Magyar tribes left their territories east of the Carpathian Mountains, invaded the Carpathian Basin and started to occupy the territory gradually around 896.
Kingdom of Hungary (1000–1918):
Following the disintegration of the Great Moravian Empire at the turn of the 10th century, the Hungarians annexed the territory comprising modern Slovakia. After their defeat on the Lech River they abandoned their nomadic ways; they settled in the center of the Carpathian valley, adopted Christianity and began to build a new state—the Hungarian kingdom.

During the revolution of 1848–49, the Slovaks supported the Austrian Emperor, hoping for independence from the Hungarian part of the Dual Monarchy, but they failed to achieve their aim. Thereafter relations between the nationalities deteriorated, culminating in the secession of Slovakia from Hungary after World War I.
Czechoslovakia (1918–1939):
On 18 October 1918, Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk, Milan Rastislav Štefánik and Edvard Beneš declared in Washington, D.C. the independence for the territories of Bohemia, Moravia, Silesia, Upper Hungary and Carpathian Ruthenia from the Austro-Hungarian Empire and proclaimed a common state, Czechoslovakia. In 1919, during the chaos following the break-up of Austria-Hungary, Czechoslovakia was formed with numerous Germans, Slovaks, Hungarians and Ruthenians within the newly set borders. The borders were set by the Treaty of Saint Germain and Treaty of Trianon. In the peace following the World War, Czechoslovakia emerged as a sovereign European state. It provided what were at the time rather extensive rights to its minorities, at least on paper.
