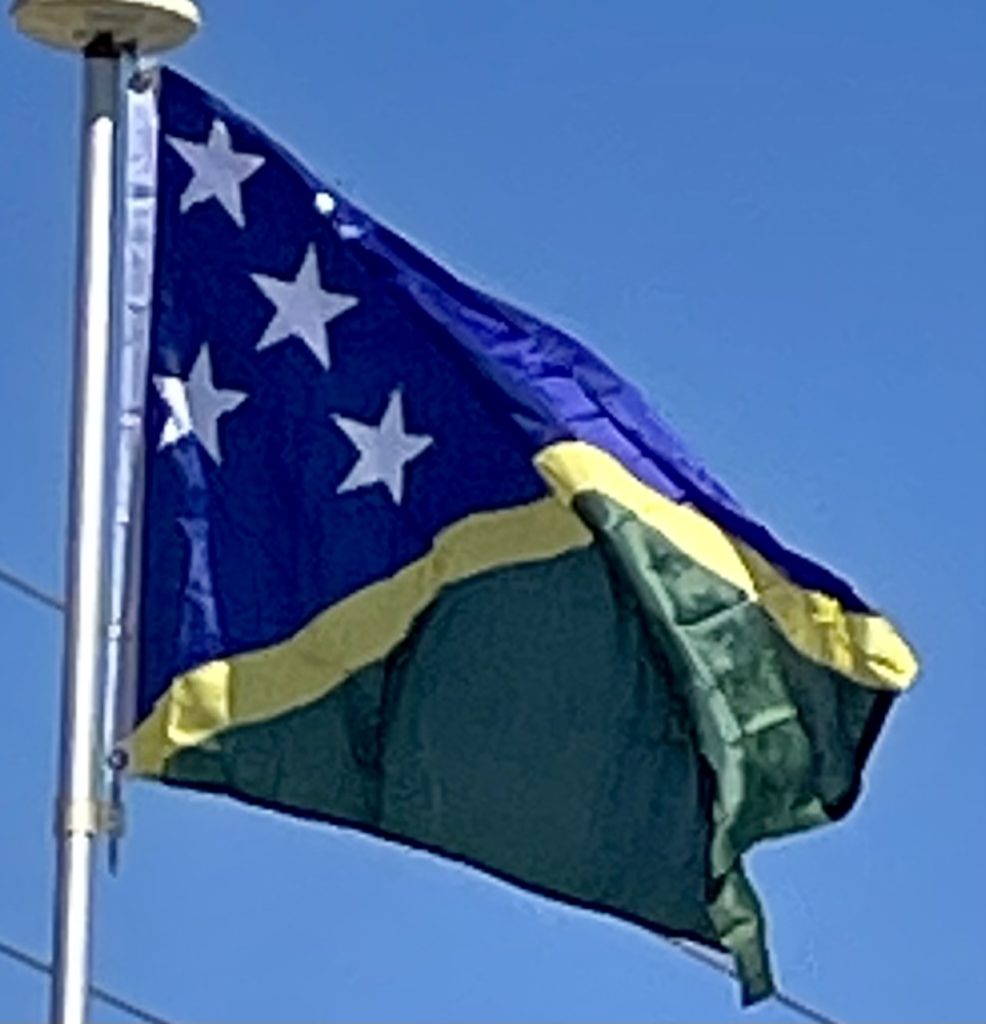
Introduction:
Solomon Islands is a sovereign country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and northwest of Vanuatu. It has a land area of 28,400 square kilometers (11,000 sq mi), and a population of 652,858. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the Solomon Islands archipelago, which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the North Solomon Islands (a part of Papua New Guinea), but excludes outlying islands, such as the Santa Cruz Islands and Rennell and Bellona.
The islands have been settled since at least some time between 30,000 and 28,800 BC, with later waves of migrants, notably the Lapita people, mixing and producing the modern indigenous Solomon Islanders population. In 1568, the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña was the first European to visit them, naming them the Islas Salomón. Mendaña returned decades later, in 1595, and another Spanish expedition, led by Portuguese navigator Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, visited the Solomons in 1606. Britain defined its area of interest in the Solomon Islands archipelago in June 1893, when Captain Gibson R.N., of HMS Curacoa, declared the southern Solomon Islands a British protectorate. During World War II, the Solomon Islands campaign (1942–1945) saw fierce fighting between the United States, Commonwealth forces and the Empire of Japan, including the Battle of Guadalcanal.

The official name of the then-British administration was changed from the British Solomon Islands Protectorate to the Solomon Islands in 1975, and self-government was achieved the following year. Independence was obtained, and the name changed to just “Solomon Islands” (without the definite article), in 1978. At independence, Solomon Islands became a constitutional monarchy. The Queen of Solomon Islands is Elizabeth II, represented by the Governor-General.
History:
Prehistory:
The Solomons were first colonized by people coming from the Bismarck Islands and New Guinea during the Pleistocene era c. 30,000-28,000 BCE. The ethnic identity of these early peoples is unclear.

From c. 1200-800 BCE Austronesian Lapita people began arriving from the Bismarcks with their characteristic ceramics.
Arrival of Europeans (1568–1886):
The first European to visit the islands was the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira, sailing from Peru in 1568. Landing on Santa Isabel on 7 February, Mendaña explored several of the other islands including Makira, Guadalcanal and Malaita. Relations with the native Solomon Islanders were initially cordial, though often soured as time went by. As a result, Mendaña returned to Peru in August 1568. He returned to the Solomons with a larger crew on a second voyage in 1595, aiming to colonize the islands. They landed on Nendö in the Santa Cruz Islands and established a small settlement at Gracioso Bay. However the settlement failed due to poor relations with the native peoples and epidemics of disease amongst the Spanish which caused numerous deaths, with Mendaña himself dying in October.
