At the time of the British occupation and colonization in 1803, the indigenous population was estimated at between 3,000 and 10,000. Historian Lyndall Ryan’s analysis of population studies led her to conclude that there were about 7,000 spread throughout the island’s nine nations; Nicholas Clements, citing research by N.J.B. Plomley and Rhys Jones, settled on a figure of 3,000 to 4,000. They engaged in fire-stick farming, hunted game including kangaroo and wallabies, caught seals, mutton-birds, shellfish and fish and lived as nine separate “nations” on the island, which they knew as “Trouwunna”.
European Arrival and Governance:
The first reported sighting of Tasmania by a European was on 24 November 1642 by Dutch explorer Abel Tasman, who landed at today’s Blackman Bay. More than a century later, in 1772, a French expedition led by Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne landed at (nearby but different) Blackmans Bay, and the following year Tobias Furneaux became the first Englishman to land in Tasmania when he arrived at Adventure Bay, which he named after his ship HMS Adventure. Captain James Cook also landed at Adventure Bay in 1777. Matthew Flinders and George Bass sailed through Bass Strait in 1798–99, determining for the first time that Tasmania was an island.
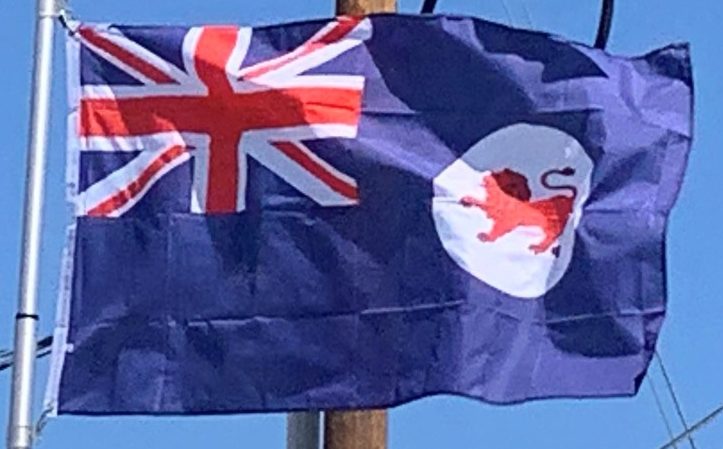
Sealers and whalers based themselves on Tasmania’s islands from 1798, and in August 1803 New South Wales Governor Philip King sent Lieutenant John Bowen to establish a small military outpost on the eastern shore of the Derwent River in order to forestall any claims to the island by French explorers who had been exploring the southern Australian coastline. Bowen, who led a party of 49, including 21 male and three female convicts, named the camp Risdon. Several months later a second settlement was established by Captain David Collins, with 308 convicts, 3.1 miles to the south in Sullivans Cove on the western side of the Derwent, where fresh water was more plentiful. The latter settlement became known as Hobart Town or Hobarton, later shortened to Hobart, after the British Colonial Secretary of the time, Lord Hobart. The settlement at Risdon was later abandoned. Left on their own without further supplies, the Sullivans Cove settlement suffered severe food shortages and by 1806 its inhabitants were starving, with many resorting to scraping seaweed off rocks and scavenging washed-up whale blubber from the shore to survive.
A smaller colony was established at Port Dalrymple on the Tamar River in the island’s north in October 1804 and several other convict-based settlements were established, including the particularly harsh penal colonies at Port Arthur in the southeast and Macquarie Harbour on the West Coast. Tasmania was eventually sent 75,000 convicts—four out of every ten people transported to Australia. By 1819 the Aboriginal and British population reached parity with about 5000 of each, although among the colonists men outnumbered women four to one. Wealthy middle-class free settlers began arriving in large numbers from 1820, lured by the promise of land grants and free convict labor.
