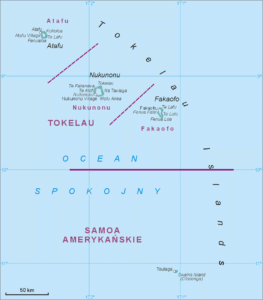
Swains Island was claimed by the United States pursuant to the Guano Islands Act, as were the other three islands of Tokelau; the latter three claims were ceded to Tokelau by treaty in 1979. In the draft constitution of Tokelau subject to the Tokelauan self-determination referendum in 2006, Olohega (Swains Island) was also claimed as a part of Tokelau, though the claim was surrendered in the same 1979 treaty. This established a clearly defined boundary between American Samoa and Tokelau.
Tokelau’s claim to Swains is generally comparable to the Marshall Islands‘ claim to US-administered Wake Island, but the re-emergence of this somewhat dormant issue has been an unintended result of the United Nations’ recent efforts to promote decolonization in Tokelau. Tokelauans have proved somewhat reluctant to push their national identity in the political realm: recent decolonization moves have mainly been driven from outside for ideological reasons. But at the same time, Tokelauans are reluctant to disown their common cultural identity with Swains Islanders who speak their language.
Economy:
According to the US Central Intelligence Agency’s list of countries by GDP (PPP) Tokelau has the smallest economy in the world. Tokelau has an annual purchasing power of about US$1,000 (€674) per capita. The government is almost entirely dependent on subsidies from New Zealand. It has annual revenues of less than US$500,000 (€336,995) against expenditures of some US$2.8 million (€1.9 million). The deficit is made up by aid from New Zealand.

Tokelau annually exports around US$100,000 (€67,000) of stamps, copra and woven and carved handicrafts and imports over US$300,000 (€202,000) of foodstuffs, building materials, and fuel to, and from, New Zealand. New Zealand also pays directly for the cost of medical and education services. Local industries include small-scale enterprises for copra production, wood work, plaited craft goods, stamps, coins, and fishing. Agriculture and livestock produces coconuts, copra, breadfruit, papayas, bananas, figs, pigs, poultry and a few goats. Many Tokelauans live in New Zealand and support their families in Tokelau through remittances.
Transportation:
Tokelau is served by the MV Mataliki, delivered new in 2016 as a replacement of the smaller MV Tokelau and jointly managed by the Tokelau Transport Department and the company Transport and Marine. The vessel, which has a capacity of 60 passengers on international cruises and 120 for transport between the atolls of Tokelau, operates fortnightly between Tokelau and Apia, with the trip taking a little over a day. A dedicated cargo vessel, the MV Kalopaga, will enter service in 2018 and replace chartered freight vessels.

Ships load and unload cargo by motoring up to the down-wind (leeward) side of the islet where the people live and maintaining station, by intermittent use of engines, close to the reef edge so that a landing barge can be motored out to transfer cargo to or from the shore. On returning to shore, the barge negotiates a narrow channel through the reef to the beach. Usually this landing is subject to ocean swell and beaching requires considerable skill and, often, coral abrasions to bodies. When bad weather prevents the barge making the trip, the ship stands off to wait for suitable weather or goes off to one of the other atolls to attempt to load or unload its passengers or cargo, or both.
