



The majority of the population reside on the island of Trinidad, and this is thus the location of largest towns and cities. There are four major municipalities in Trinidad: the capital Port of Spain, San Fernando, Arima and Chaguanas. The main town on Tobago is Scarborough.
Trinidad and Tobago is the most developed nation and one of the wealthiest in the Caribbean and is listed in the top 40 (2010 information) of the 70 high-income countries in the world. Its gross national income per capita of US$20,070 (2014 gross national income at Atlas Method) is one of the highest in the Caribbean. In November 2011, the OECD removed Trinidad and Tobago from its list of developing countries.
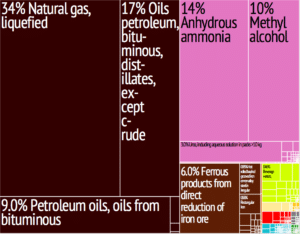
Trinidad’s economy is strongly influenced by the petroleum industry. Tourism and manufacturing are also important to the local economy. Tourism is a growing sector, particular on Tobago, although proportionately it is much less important than in many other Caribbean islands. Agricultural products include citrus and cocoa. It also supplies manufactured goods, notably food, beverages, and cement, to the Caribbean region.
The transport system in Trinidad and Tobago consists of a dense network of highways and roads across both major islands, ferries connecting Port of Spain with Scarborough and San Fernando, and international airports on both islands. The Uriah Butler Highway, Churchill Roosevelt Highway and the Sir Solomon Hochoy Highway links the island of Trinidad together, whereas the Claude Noel Highway is the only major highway in Tobago. Public transportation options on land are public buses, private taxis and minibuses. By sea, the options are inter-island ferries and inter-city water taxis.

The island of Trinidad is served by Piarco International Airport located in Piarco, which opened on 8 January 1931. Elevated at 17.4 metres (57 ft) above sea level it comprises an area of 680 hectares (1,700 acres) and has a runway of 3,200 metres (10,500 ft). The airport consists of two terminals, the North Terminal and the South Terminal. The older South Terminal underwent renovations in 2009 for use as a VIP entrance point during the 5th Summit of the Americas. The North Terminal was completed in 2001, and consists of 14-second-level aircraft gates with jetways for international flights, two ground-level domestic gates and 82 ticket counter positions.

The Island of Tobago is served by the A.N.R. Robinson International Airport in Crown Point. This airport has regular services to North America and Europe. There are regular flights between the two islands, with fares being heavily subsidized by the Government.
The flag of Trinidad and Tobago was adopted upon independence from the United Kingdom on 31 August 1962. Designed by Carlisle Chang (1921–2001), the flag of Trinidad and Tobago was chosen by the independence committee of 1962. Red, black and white symbolize fire (the sun, representing courage), earth (representing dedication) and water (representing purity and equality).