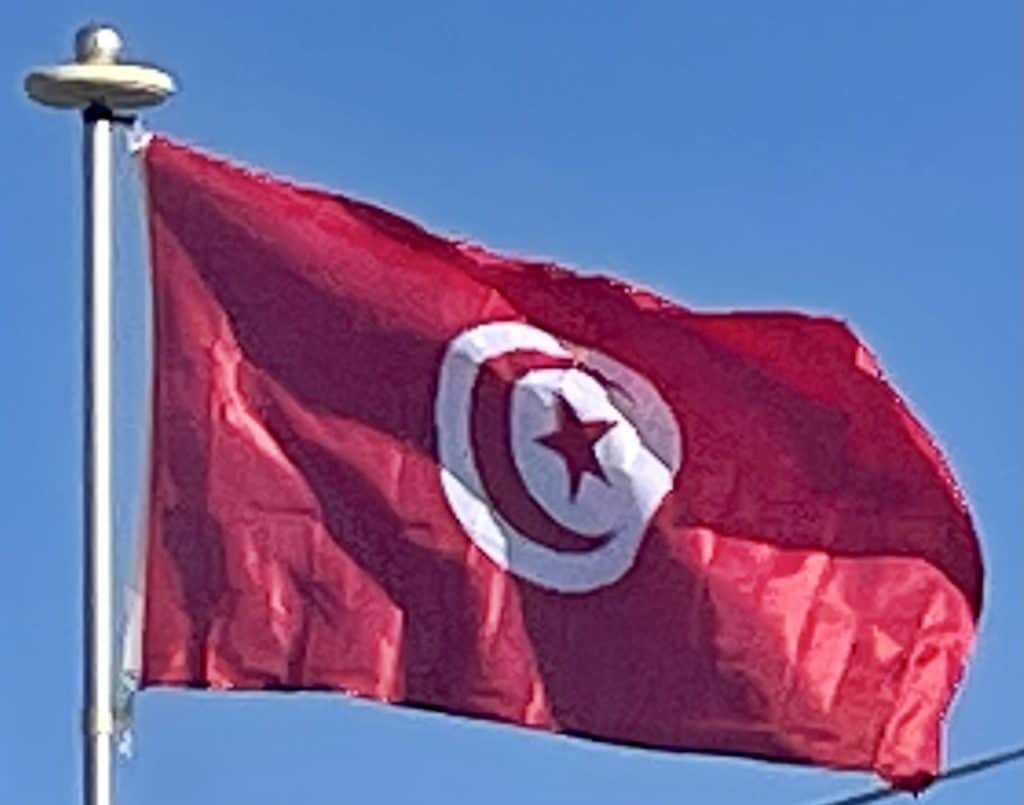
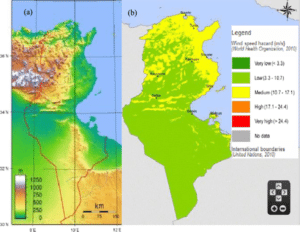
Though it is relatively small in size, Tunisia has great environmental diversity due to its north–south extent. Its east–west extent is limited. Differences in Tunisia, like the rest of the Maghreb, are largely north–south environmental differences defined by sharply decreasing rainfall southward from any point. The Dorsal, the eastern extension of the Atlas Mountains, runs across Tunisia in a northeasterly direction from the Algerian border in the west to the Cape Bon peninsula in the east. North of the Dorsal is the Tell, a region characterized by low, rolling hills and plains, again an extension of mountains to the west in Algeria. In the Khroumerie, the northwestern corner of the Tunisian Tell, elevations reach 1,050 metres (3,440 ft) and snow occurs in winter.
The Sahel, a broadening coastal plain along Tunisia’s eastern Mediterranean coast, is among the world’s premier areas of olive cultivation. Inland from the Sahel, between the Dorsal and a range of hills south of Gafsa, are the Steppes. Much of the southern region is semi-arid and desert.
Economy:
Ranked the most competitive economy in Africa by the World Economic Forum in 2009;[119] Tunisia is an export-oriented country in the process of liberalizing and privatizing an economy that, while averaging 5% GDP growth since the early 1990s, has suffered from corruption benefiting politically connected elites. Tunisia’s Penal Code criminalizes several forms of corruption, including active and passive bribery, abuse of office, extortion and conflicts of interest, but the anti-corruption framework is not effectively enforced. However, according to the Corruption Perceptions Index published annually by Transparency International, Tunisia was ranked the least corrupt North African country in 2016, with a score of 41. Tunisia has a diverse economy, ranging from agriculture, mining, manufacturing, and petroleum products, to tourism, which accounted for 7% of the total GDP and 370,000 jobs in 2009. In 2008 it had an economy of US$41 billion in nominal terms, and $82 billion in PPP.
The agricultural sector accounts for 11.6% of the GDP, industry 25.7%, and services 62.8%. The industrial sector is mainly made up of clothing and footwear manufacturing, production of car parts, and electric machinery. Although Tunisia managed an average 5% growth over the last decade it continues to suffer from a high unemployment especially among youth.
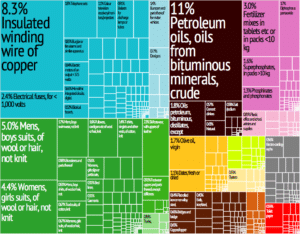
The European Union remains Tunisia’s first trading partner, currently accounting for 72.5% of Tunisian imports and 75% of Tunisian exports. Tunisia is one of the European Union’s most established trading partners in the Mediterranean region and ranks as the EU’s 30th largest trading partner. Tunisia was the first Mediterranean country to sign an Association Agreement with the European Union, in July 1995, although even before the date of entry came into force, Tunisia started dismantling tariffs on bilateral EU trade. Tunisia finalized the tariffs dismantling for industrial products in 2008 and therefore was the first non-EU Mediterranean country to enter in a free trade area with EU.
Transportation:
The country maintains 19,232 kilometres (11,950 mi) of roads, with three highways: the A1 from Tunis to Sfax (works ongoing for Sfax-Libya), A3 Tunis-Beja (works ongoing Beja – Boussalem, studies ongoing Boussalem – Algeria) and A4 Tunis – Bizerte.

