In 2013, widespread protests erupted in many Turkish provinces, sparked by a plan to demolish Gezi Park but soon growing into general anti-government dissent. On 15 July 2016, an unsuccessful coup attempt tried to oust the government. As a reaction to the failed coup d’état, the government carried out mass purges.
Between 9 October – 25 November 2019, Turkey conducted a military offensive into north-eastern Syria.
Geography:
Turkey is a transcontinental country bridging Southeastern Europe and Western Asia. Asian Turkey, which includes 97 percent of the country’s territory, is separated from European Turkey by the Bosphorus, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles. European Turkey comprises only 3 percent of the country’s territory. Turkey covers an area of 783,562 square kilometres (302,535 square miles), of which 755,688 square kilometres (291,773 square miles) is in Asia and 23,764 square kilometres (9,175 square miles) is in Europe. The country is encircled by seas on three sides: the Aegean Sea to the west, the Black Sea to the north and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Turkey also contains the Sea of Marmara in the northwest.
Turkey is divided into seven geographical regions: Marmara, Aegean, Black Sea, Central Anatolia, Eastern Anatolia, Southeastern Anatolia and the Mediterranean. The uneven north Anatolian terrain running along the Black Sea resembles a long, narrow belt. This region comprises approximately one-sixth of Turkey’s total land area. As a general trend, the inland Anatolian plateau becomes increasingly rugged as it progresses eastward.
The Eastern Anatolia Region mostly corresponds to the western part of the Armenian Highlands (the plateau situated between the Anatolian Plateau in the west and the Lesser Caucasus in the north) and contains Mount Ararat, Turkey’s highest point at 5,137 metres (16,854 feet), and Lake Van, the largest lake in the country. Eastern Turkey has a mountainous landscape and is home to the sources of rivers such as the Euphrates, Tigris and Aras. The Southeastern Anatolia Region includes the northern plains of Upper Mesopotamia.
Economy:
Turkey is a newly industrialized country, with an upper-middle income economy, which is the twentieth-largest in the world by nominal GDP, and the eleventh-largest by PPP. According to World Bank estimates, Turkey’s GDP per capita by PPP is $32,278 in 2021, and approximately 14.4% of Turks lived below the national poverty line in 2018. Unemployment in Turkey was 13.6% in 2019, and the middle class population in Turkey rose from 18% to 41% of the population between 1993 and 2010 according to the World Bank. The EU–Turkey Customs Union in 1995 led to an extensive liberalization of tariff rates, and forms one of the most important pillars of Turkey’s foreign trade policy.
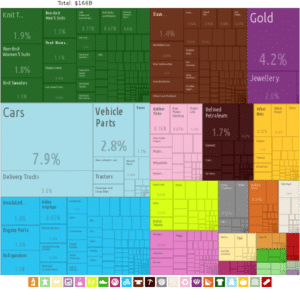
The automotive industry in Turkey is sizeable, and produced over 1.3 million motor vehicles in 2015, ranking as the 14th largest producer in the world. Turkish shipyards are highly regarded both for the production of chemical and oil tankers up to 10,000 dwt and also for their mega yachts. Turkish brands like Beko and Vestel are among the largest producers of consumer electronics and home appliances in Europe, and invest a substantial amount of funds for research and development in new technologies related to these fields.

