In 637, Julfar (in the area of today’s Ras Al Khaimah) was an important port that was used as a staging post for the Islamic invasion of the Sasanian Empire. The area of the Al Ain/Buraimi Oasis was known as Tu’am and was an important trading post for camel routes between the coast and the Arabian interior.
The earliest Christian site in the UAE was first discovered in the 1990s, an extensive monastic complex on what is now known as Sir Bani Yas Island and which dates back to the 7th century. Thought to be Nestorian and built in 600 CE, the church appears to have been abandoned peacefully in 750 CE. It forms a rare physical link to a legacy of Christianity which is thought to have spread across the peninsula from 50 to 350 CE following trade routes. Certainly, by the 5th century, Oman had a bishop named John – the last bishop of Oman being Etienne, in 676 CE.
Portuguese era:

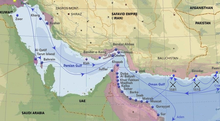
With the expansion of European colonial empires, Portuguese, English and Dutch forces appeared in the Persian Gulf region. By the 18th century, the Bani Yas confederation was the dominant force in most of the area now known as Abu Dhabi, while the Northern Al Qawasim (Al Qasimi) dominated maritime commerce. The Portuguese maintained an influence over the coastal settlements, building forts in the wake of the bloody 16th-century conquests of coastal communities by Albuquerque and the Portuguese commanders who followed him – particularly on the east coast at Muscat, Sohar and Khor Fakkan.
The southern coast of the Persian Gulf was known to the British as the “Pirate Coast“, as boats of the Al Qawasim federation harassed British-flagged shipping from the 17th century into the 19th. The charge of piracy is disputed by modern Emirati historians, including the current Ruler of Sharjah, Sheikh Sultan Al Qasimi, in his 1986 book The Myth of Arab Piracy in the Gulf.
British expeditions to protect their Indian trade routes led to campaigns against Ras Al Khaimah and other harbors along the coast, including the Persian Gulf Campaign of 1809 and the more successful campaign of 1819. The following year, Britain and a number of local rulers signed a maritime truce, giving rise to the term Trucial States, which came to define the status of the coastal emirates. A further treaty was signed in 1843 and, in 1853 the Perpetual Maritime Truce was agreed. To this was added the ‘Exclusive Agreements’, signed in 1892, which made the Trucial States a British protectorate.