Objectives:
The main objectives of the United Nations are to provide for and protect the following:
- Peacekeeping and Security
- Human Rights
- Economic Development and Humanitarian Assistance

UN Forces Training Exercise in Chile
Funding:
Top 25 contributors to the United Nations budget for the period 2019 – 2021
- United States (22%)
- China (12.005%)
- Japan (8.564%)
- Germany (6.090%)
- United Kingdom (4.567%)
- France (4.427%)
- Italy (3.307%)
- Brazil (2.948%)
- Canada (2.734%)
- Russia (2.405%)
- South Korea (2.267%)
- Australia (2.210%)
- Spain (2.146%)
- Turkey (1.371%)
- Netherlands (1.356%)
- Mexico (1.292%)
- Saudi Arabia (1.172%)
- Switzerland (1.151%)
- Argentina (0.915%)
- Sweden (0.906%)
- India (0.834%)
- Belgium (0.821%)
- Poland (0.802%)
- Algeria (0.788%)
- Norway (0.754%)
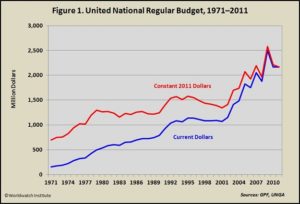
The UN is financed from assessed and voluntary contributions from member states. The General Assembly approves the regular budget and determines the assessment for each member. This is broadly based on the relative capacity of each country to pay, as measured by its gross national income (GNI), with adjustments for external debt and low per capita income. The two-year budget for 2012–13 was $5.512 billion in total.
The Assembly has established the principle that the UN should not be unduly dependent on any one member to finance its operations. Thus, there is a “ceiling” rate, setting the maximum amount that any member can be assessed for the regular budget. In December 2000, the Assembly revised the scale of assessments in response to pressure from the United States. As part of that revision, the regular budget ceiling was reduced from 25% to 22%. For the least developed countries (LDCs), a ceiling rate of 0.01% is applied. In addition to the ceiling rates, the minimum amount assessed to any member nation (or “floor” rate) is set at 0.001% of the UN budget ($55,120 for the two year budget 2013–2014).
A large share of the UN’s expenditure addresses its core mission of peace and security, and this budget is assessed separately from the main organizational budget. The peacekeeping budget for the 2015–16 fiscal year was $8.27 billion, supporting 82,318 troops deployed in 15 missions around the world. UN peace operations are funded by assessments, using a formula derived from the regular funding scale that includes a weighted surcharge for the five permanent Security Council members, who must approve all peacekeeping operations. This surcharge serves to offset discounted peacekeeping assessment rates for less developed countries. In 2017, the top eight providers of assessed financial contributions to UN peacekeeping operations were the United States (28.47%), China (10.25%), Japan (9.68%), Germany (6.39%), France (6.28%), United Kingdom (5.77%), Russian Federation (3.99%) and Italy (3.75%).
Special UN programmed not included in the regular budget, such as UNICEF and the World Food Programme, are financed by voluntary contributions from member governments, corporations, and private individuals.
The Flag:
The flag of the United Nations was adopted on December 7, 1946, and consists of the official emblem of the United Nations in white on a blue background.

Design:
The emblem’s design is described as:
