The Treaty of Saint-Germain of 1919 (for Hungary the Treaty of Trianon of 1920) confirmed and consolidated the new order of Central Europe which to a great extent had been established in November 1918, creating new states and altering others. The German-speaking parts of Austria which had been part of Austria-Hungary were reduced to a rump state named The Republic of German-Austria (German: Republik Deutschösterreich). The desire for Anschluss (annexation of Austria to Germany) was a popular opinion shared by all social circles in both Austria and Germany. On 12 November, German-Austria was declared a republic, and named Social Democrat Karl Renner as provisional chancellor. On the same day it drafted a provisional constitution that stated that “German-Austria is a democratic republic” (Article 1) and “German-Austria is an integral part of the German reich” (Article 2). The Treaty of Saint Germain and the Treaty of Versailles explicitly forbid union between Austria and Germany. The treaties also forced German-Austria to rename itself as “Republic of Austria” which consequently led to the first Austrian Republic.
Over 3 million German-speaking Austrians found themselves living outside the new Austrian Republic as minorities in the newly formed or enlarged states of Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Hungary, and Italy. These included the provinces of South Tyrol (which became part of Italy) and German Bohemia (Czechoslovakia). The status of German Bohemia (Sudetenland) later played a role in sparking the Second World War.
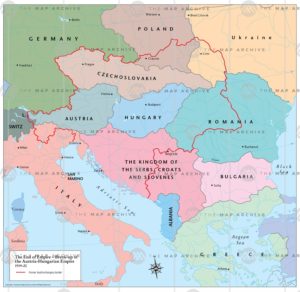
The status of South Tyrol was a lingering problem between Austria and Italy until it was officially settled by the 1980s with a great degree of autonomy being granted to it by the Italian national government. Between 1918 and 1919, Austria was known as the State of German Austria (Staat Deutschösterreich). Not only did the Entente powers forbid German Austria to unite with Germany, but they also rejected the name German Austria in the peace treaty to be signed; it was, therefore, changed to Republic of Austria in late 1919.
The border between Austria and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (later Yugoslavia) was settled with the Carinthian Plebiscite in October 1920 and allocated the major part of the territory of the former Austro-Hungarian Crownland of Carinthia to Austria. This set the border on the Karawanken mountain range, with many Slovenes remaining in Austria.
Interwar Period and World War II:
After the war, inflation began to devalue the Krone, which was still Austria’s currency. In autumn 1922, Austria was granted an international loan supervised by the League of Nations. The purpose of the loan was to avert bankruptcy, stabilize the currency, and improve Austria’s general economic condition. The loan meant that Austria passed from an independent state to the control exercised by the League of Nations. In 1925, the Schilling was introduced, replacing the Krone at a rate of 10,000:1. Later, it was nicknamed the “Alpine dollar” due to its stability. From 1925 to 1929, the economy enjoyed a short high before nearly crashing after Black Tuesday.
