It also encompasses a number of oceanic archipelagos, such as Fernando de Noronha, Rocas Atoll, Saint Peter and Paul Rocks, and Trindade and Martim Vaz. Its size, relief, climate, and natural resources make Brazil geographically diverse.
Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world, and third largest in the Americas, with a total area of 3,287,956 square miles, including 21,411 square miles of water. It spans four time zones; from UTC−5 comprising the state of Acre and the westernmost portion of Amazonas, to UTC−4 in the western states, to UTC−3 in the eastern states (the national time) and UTC−2 in the Atlantic islands.
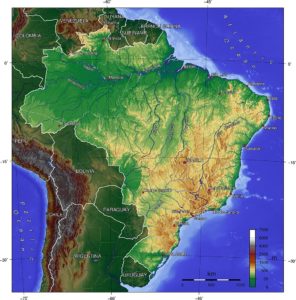
Brazil is the only country in the world that has the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn running through it. Brazilian topography is also diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. Much of the terrain lies between 660 feet) and 2,600 feet in elevation. The main upland area occupies most of the southern half of the country. The northwestern parts of the plateau consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, rounded hills.
The southeastern section is more rugged, with a complex mass of ridges and mountain ranges reaching elevations of up to 3,900 feet. These ranges include the Mantiqueira and Espinhaço mountains and the Serra do Mar.

In the north, the Guiana Highlands form a major drainage divide, separating rivers that flow south into the Amazon Basin from rivers that empty into the Orinoco River system, in Venezuela, to the north. The highest point in Brazil is the Pico da Neblina at 9,823 feet, and the lowest is the Atlantic Ocean.
Brazil has a dense and complex system of rivers, one of the world’s most extensive, with eight major drainage basins, all of which drain into the Atlantic. Major rivers include the Amazon (the world’s second-longest river and the largest in terms of volume of water), the Paraná and its major tributary the Iguaçu (which includes the Iguazu Falls), the Negro, São Francisco, Xingu, Madeira and Tapajós rivers.
Economy:
Brazil is the largest national economy in Latin America, the world’s ninth largest economy and the eighth largest in purchasing power parity (PPP) according to the 2018 estimates. Brazil has a mixed economy with abundant natural resources. After rapid growth in preceding decades, the country entered an ongoing recession in 2014 amid a political corruption scandal and nationwide protests.
The country has been expanding its presence in international financial and commodities markets, and is one of a group of four emerging economies called the BRIC countries. Brazil has been the world’s largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years.
Brazil’s diversified economy includes agriculture, industry, and a wide range of services. Agriculture and allied sectors like forestry, logging and fishing accounted for 5.1% of the gross domestic product in 2007. Brazil is one of the largest producer of oranges, coffee, sugar cane, cassava and sisal, soybeans and papayas.
