The US State Department and the US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), along with the British government, also played a strong role in influencing political control in Guyana during this time. The American government supported Forbes Burnham during the early years of independence because Cheddi Jagan was identified as a Marxist. They provided secret financial support and political campaign advice to Burnham’s People’s National Congress, to the detriment of the Jagan-led People’s Progressive Party, which was mostly supported by Guyanese of East Indian background.
In 1974, the Guyana government leased 1,500 hectares (3,800 acres) of land to Peoples Temple, an American new religious movement, led by pastor Jim Jones.

The settlement, informally called “Jonestown”, eventually grew to a population of about 1,000 people, mostly emigrated from the United States. In 1978, Guyana received worldwide attention when 909 people died in a mass murder/suicide in Jonestown by drinking cyanide-laced Flavor Aid. A day prior, U.S. congressman Leo Ryan had visited and toured the settlement as part of an investigation. As he was preparing to leave at the Port Kaituma airstrip, a group of Peoples Temple members pulled up and opened fire on the visiting delegation, killing Ryan and four other people.
In May 2008, President Bharrat Jagdeo was a signatory to the UNASUR Constitutive Treaty of the Union of South American Nations. The Guyanese government officially ratified the treaty in 2010.
Geography:
The country can be divided into five natural regions; a narrow and fertile marshy plain along the Atlantic coast (low coastal plain) where most of the population lives; a white sand belt more inland (hilly sand and clay region), containing most of Guyana’s mineral deposits; the dense rain forests (Forested Highland Region) in the southern part of the country; the drier savannah areas in the south-west; and the smallest interior lowlands (interior savannah) consisting mostly of mountains that gradually rise to the Brazilian border.
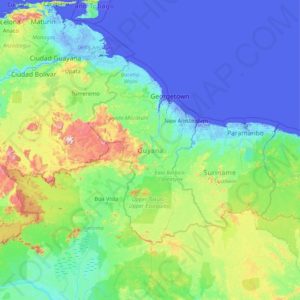
Some of Guyana’s highest mountains are Mount Ayanganna (2,042 metres or 6,699 feet), Monte Caburaí (1,465 metres or 4,806 feet) and Mount Roraima (2,772 metres or 9,094 feet – the highest mountain in Guyana) on the Brazil-Guyana-Venezuela tripoint border, part of the Pakaraima range. Mount Roraima and Guyana’s table-top mountains (tepuis) are said to have been the inspiration for Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s 1912 novel The Lost World. There are also many volcanic escarpments and waterfalls, including Kaieteur Falls which is believed to be the largest single-drop waterfall in the world.

North of the Rupununi River lies the Rupununi savannah, south of which lie the Kanuku Mountains.
The four longest rivers are the Essequibo at 1,010 kilometres (628 mi) long, the Courentyne River at 724 kilometres (450 mi), the Berbice at 595 kilometres (370 mi), and the Demerara at 346 kilometres (215 mi). The Courentyne river forms the border with Suriname. At the mouth of the Essequibo are several large islands, including the 145 km (90 mi) wide Shell Beach along the northwest coast, which is also a major breeding area for sea turtles (mainly leatherbacks) and other wildlife.
Economy:
The main economic activities in Guyana are agriculture (production of rice and Demerara sugar), bauxite and gold mining, timber, shrimp fishing and minerals. The sugar industry, which accounts for 28% of all export earnings, is largely run by the company GuySuCo, which employs more people than any other industry. Many industries have a large foreign investment. For example, the American company Reynolds Metals and the British-Australian Rio Tinto’s Rio Tinto Alcan subsidiary are heavily invested in Guyana’s mineral industry; the Korean/Malaysian Barama Company has a large stake in the logging industry. Since 2015, foreign companies have made several significant deep water oil discoveries.
