The conflict between Hmong rebels and the LPDR continued in key areas of Laos, including in Saysaboune Closed Military Zone, Xaisamboune Closed Military Zone near Vientiane Province and Xieng Khouang Province. From 1975 to 1996, the United States resettled some 250,000 Lao refugees from Thailand, including 130,000 Hmong
On 2 December 2015, Laos celebrated the 40th anniversary of the establishment of the republic.
Geography:
Laos is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. Its thickly forested landscape consists mostly of rugged mountains, the highest of which is Phou Bia at 2,818 metres (9,245 ft), with some plains and plateaus. The Mekong River forms a large part of the western boundary with Thailand, where the mountains of the Annamite Range form most of the eastern border with Vietnam and the Luang Prabang Range the northwestern border with the Thai highlands. There are two plateau, the Xiangkhoang in the north and the Bolaven Plateau at the southern end. The climate is tropical and influenced by the monsoon pattern.

There is a distinct rainy season from May to November, followed by a dry season from December to April. Local tradition holds that there are three seasons (rainy, cold and hot) as the latter two months of the climatologically defined dry season are noticeably hotter than the earlier four months. The capital and largest city of Laos is Vientiane and other major cities include Luang Prabang, Savannakhet, and Pakse.
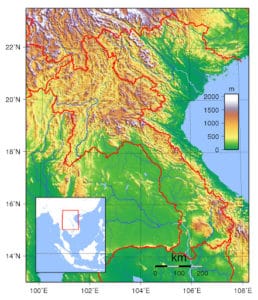
In 1993 the Laos government set aside 21 percent of the nation’s land area for habitat conservation preservation. The country is one of four in the opium poppy growing region known as the “Golden Triangle“. According to the October 2007 UNODC fact book Opium Poppy Cultivation in South East Asia, the poppy cultivation area was 15 square kilometres (5.8 sq mi), down from 18 square kilometres (6.9 sq mi) in 2006.
Laos can be considered to consist of three geographical areas: north, central, and south.
Economy:
The Lao economy depends heavily on investment and trade with its neighbors, Thailand, Vietnam, and, especially in the north, China. Pakxe has also experienced growth based on cross-border trade with Thailand and Vietnam. In 2009, despite the fact that the government is still officially communist, the Obama administration in the US declared Laos was no longer a Marxist–Leninist state and lifted bans on Laotian companies receiving financing from the US Export-Import Bank. In 2011, the Lao Securities Exchange began trading. In 2012, the government initiated the creation of the Laos Trade Portal, a website incorporating all information traders need to import and export goods into the country.
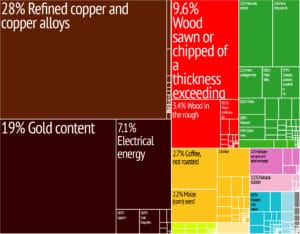
In 2016, China was the biggest foreign investor in Laos’s economy, having invested in US$5.395 billion since 1989, according to Laos Ministry of Planning and Investment 1989–2014 report. Thailand (invested US$4.489 billion) and Vietnam (invested US$3.108 billion) are the second and third largest investors respectively.
