Luxembourg is a founding member of the European Union, OECD, United Nations, NATO, and Benelux. The city of Luxembourg, which is the country’s capital and largest city, is the seat of several institutions and agencies of the EU. Luxembourg served on the United Nations Security Council for the years 2013 and 2014, which was a first in the country’s history. As of 2020, Luxembourg citizens had visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to 187 countries and territories, ranking the Luxembourgish passport fifth in the world, tied with Denmark and Spain.
History:
The recorded history of Luxembourg begins with the acquisition of Lucilinburhuc (today Luxembourg Castle) situated on the Bock rock by Siegfried, Count of Ardennes, in 963 through an exchange act with St. Maximin’s Abbey, Trier. Around this fort, a town gradually developed, which became the center of a state of great strategic value.

Duchy:
In the 14th and early 15th centuries, three members of the House of Luxembourg reigned as Holy Roman Emperors. In 1437, the House of Luxembourg suffered a succession crisis, precipitated by the lack of a male heir to assume the throne, which led to the territories being sold by Duchess Elisabeth to Philip the Good of Burgundy.
In the following centuries, Luxembourg’s fortress was steadily enlarged and strengthened by its successive occupants, the Bourbons, Habsburgs, Hohenzollerns and the French.
19th Century:
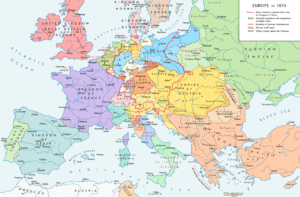
After the defeat of Napoleon in 1815, Luxembourg was disputed between Prussia and the Netherlands. The Congress of Vienna formed Luxembourg as a Grand Duchy within the German Confederation. The Dutch king became, in personal union, the grand duke. Although he was supposed to rule the grand duchy as an independent country with an administration of its own, in reality he treated it similarly to a Dutch province. The Fortress of Luxembourg was manned by Prussian troops for the German Confederation. This arrangement was revised by the 1839 First Treaty of London, from which date Luxembourg’s full independence is reckoned.

At the time of the Belgian Revolution of 1830–1839, and by the 1839 Treaty establishing full independence, Luxembourg’s territory was reduced by more than half, as the predominantly francophone western part of the country was transferred to Belgium. In 1842 Luxembourg joined the German Customs Union (Zollverein). This resulted in the opening of the German market, the development of Luxembourg’s steel industry, and expansion of Luxembourg’s railway network from 1855 to 1875, particularly the construction of the Luxembourg-Thionville railway line, with connections from there to the European industrial regions. While Prussian troops still manned the fortress, in 1861, the Passerelle was opened, the first road bridge spanning the Pétrusse river valley, connecting the Ville Haute and the main fortification on the Bock with Luxembourg railway station, opened in 1859, on the then fortified Bourbon plateau to the south.
After the Luxembourg Crisis of 1866 nearly led to war between Prussia and France, the Grand Duchy’s independence and neutrality were again affirmed by the 1867 Second Treaty of London, Prussia’s troops were withdrawn from the Fortress of Luxembourg, and its Bock and surrounding fortifications were dismantled.
