The largest towns are Luxembourg, Esch-sur-Alzette, Dudelange, and Differdange.

To the east, Luxembourg borders the German Bundesländer of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland, and to the south, it borders the French région of Grand Est (Lorraine). The Grand Duchy borders the Belgian Walloon Region, in particular the latter’s provinces of Luxembourg and Liège, part of which comprises the German-speaking Community of Belgium, to the west and to the north, respectively.
The northern third of the country is known as the ‘Oesling‘, and forms part of the Ardennes. It is dominated by hills and low mountains, including the Kneiff near Wilwerdange, which is the highest point, at 560 meters (1,837 ft). Other mountains are the ‘Buurgplaaz‘ at 559 meters near Huldange and the ‘Napoléonsgaard‘ at 554 meters near Rambrouch. The region is sparsely populated, with only one town (Wiltz) with a population of more than four thousand people.
The southern two-thirds of the country is called the “Gutland“, and is more densely populated than the Oesling. It is also more diverse and can be divided into five geographic sub-regions. The Luxembourg plateau, in south-central Luxembourg, is a large, flat, sandstone formation, and the site of the city of Luxembourg. Little Switzerland, in the east of Luxembourg, has craggy terrain and thick forests. The Moselle valley is the lowest-lying region, running along the southeastern border. The Red Lands, in the far south and southwest, are Luxembourg’s industrial heartland and home to many of Luxembourg’s largest towns.
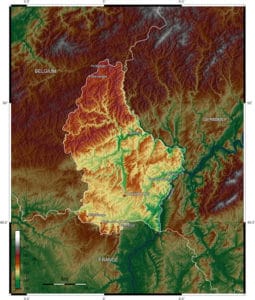
The border between Luxembourg and Germany is formed by three rivers: the Moselle, the Sauer, and the Our. Other major rivers are the Alzette, the Attert, the Clerve, and the Wiltz. The valleys of the mid-Sauer and Attert form the border between the Gutland and the Oesling.
According to the 2012 Environmental Performance Index, Luxembourg is one of the world’s best performers in environmental protection, ranking 4th out of 132 assessed countries Luxembourg also ranks 6th among the top ten most livable cities in the world by Mercer’s.
Economy:
Luxembourg’s stable and high-income market economy features moderate growth, low inflation, and a high level of innovation. Unemployment is traditionally low, although it had risen to 6.1% by May 2012, due largely to the effect of the 2008 global financial crisis. In 2011, according to the IMF, Luxembourg was the second richest country in the world, with a per capita GDP on a purchasing-power parity (PPP) basis of $80,119. Its GDP per capita in purchasing power standards was 261% of the EU average (100%) in 2019. Luxembourg is ranked 13th in The Heritage Foundation’s Index of Economic Freedom, 26th in the United Nations Human Development Index, and 4th in the Economist Intelligence Unit’s quality of life index.
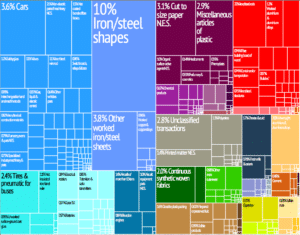
The industrial sector, which was dominated by steel until the 1960s, has since diversified to include chemicals, rubber, and other products. During the past decades, growth in the financial sector has more than compensated for the decline in steel production. Services, especially banking and finance, account for the majority of the economic output. Luxembourg is the world’s second largest investment fund center (after the United States), the most important private banking center in the Eurozone and Europe’s leading center for reinsurance companies. Moreover, the Luxembourg government has aimed to attract Internet start-ups, with Skype and Amazon being two of the many Internet companies that have shifted their regional headquarters to Luxembourg. Other high-tech companies have established themselves in Luxembourg, including 3D scanner developer/manufacturer Artec 3D.
Transportation:
Luxembourg has road, rail and air transport facilities and services. The road network has been significantly modernized in recent years with 147 km (91 mi) of motorways connecting the capital to adjacent countries. The advent of the high-speed TGV link to Paris has led to renovation of the city’s railway station and a new passenger terminal at Luxembourg Airport was opened in 2008. Luxembourg city reintroduced trams in December 2017 and there are plans to open light-rail lines in adjacent areas within the next few years.
