From 2009 through 2013, Tanzania’s per capita GDP (based on constant local currency) grew an average of 3.5% per year, higher than any other member of the East African Community (EAC) and exceeded by only nine countries in Sub-Saharan Africa: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Ghana, Lesotho, Liberia, Mozambique, Sierra Leone, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Tanzania’s largest trading partners in 2017 for its US$5.3 billion in exports were India, Vietnam, South Africa, Switzerland, and China. Its imports totaled US$8.17 billion, with India, Switzerland, Saudi Arabia, China, and the United Arab Emirates being the biggest partners.
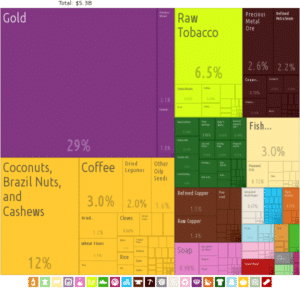
Tanzania weathered the Great Recession, which began in late 2008 or early 2009, relatively well. Strong gold prices, bolstering the country’s mining industry, and Tanzania’s poor integration into global markets helped to insulate the country from the downturn. Since the recession ended, the Tanzanian economy has expanded rapidly thanks to strong tourism, telecommunications, and banking sectors.
According to the United Nations Development Programme, however, recent growth in the national economy has benefited only the “very few”, leaving out the majority of the population. Tanzania’s 2013 Global Hunger Index was worse than any other country in the EAC except Burundi. The proportion of persons who were undernourished in 2010–12 was also worse than any other EAC country except Burundi.
In 2020, the World Bank declared the rise of the Tanzanian economy from low income to lower middle income country, as its GNI per capita increased from US$1,020 in 2018 to US$1,080 in 2019.
Transportation:

In Dar es Salaam, there is a huge project of rapid buses, Dar Rapid Transit (DART) which connects suburbs of Dar es Salaam city. The development of the DART system consists of six phases and is funded by the African Development Bank, the World Bank and the Government of Tanzania. The first phase began in April 2012, and it was completed in December 2015 and launched operations in May 2016.
Tanzania has four international airports, along with over 120 small airports or landing strips. Airport infrastructure tends to be in poor condition. Airlines in Tanzania include Air Tanzania, Precision Air, Fastjet, Coastal Aviation, and ZanAir.
Flag of Tanzania:
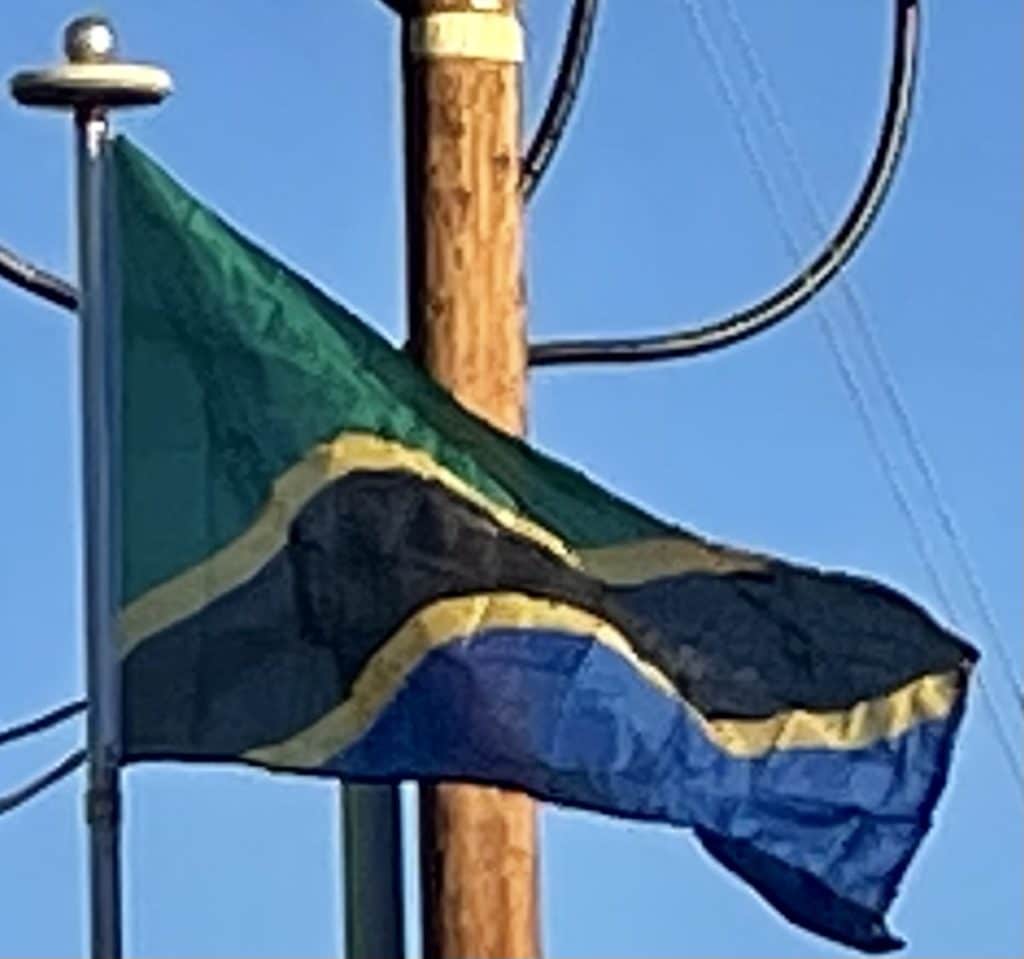
The flag of Tanzania consists of a yellow-edged black diagonal band, divided diagonally from the lower hoist-side corner, with a green upper triangle and blue lower triangle. Adopted in 1964 to replace the individual flags of Tanganyika and Zanzibar, it has been the flag of the United Republic of Tanzania since the two states merged that year. The design of the present flag incorporates the elements from the two former flags. It is one of a relatively small number of national flags incorporating a diagonal line, with other examples including the DR Congo, Namibia, Trinidad and Tobago and Brunei.

