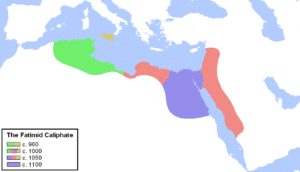
During the Middle Ages, North Africa was home to many great scholars, saints and sovereigns including Judah Ibn Quraysh, the first grammarian to suggest the Afroasiatic language family, the great Sufi masters Sidi Boumediene (Abu Madyan) and Sidi El Houari, and the Emirs Abd Al Mu’min and Yāghmūrasen. It was during this time that the Fatimids or children of Fatima, daughter of Muhammad, came to the Maghreb. These “Fatimids” went on to found a long lasting dynasty stretching across the Maghreb, Hejaz and the Levant, boasting a secular inner government, as well as a powerful army and navy, made up primarily of Arabs and Levantines extending from Algeria to their capital state of Cairo. The Fatimid caliphate began to collapse when its governors the Zirids seceded. In order to punish them the Fatimids sent the Arab Banu Hilal and Banu Sulaym against them. The resultant war is recounted in the epic Tāghribāt. In Al-Tāghrībāt the Amazigh Zirid Hero Khālīfā Al-Zānatī asks daily, for duels, to defeat the Hilalan hero Ābu Zayd al-Hilalī and many other Arab knights in a string of victories. The Zirids, however, were ultimately defeated ushering in an adoption of Arab customs and culture. The indigenous Amazigh tribes, however, remained largely independent, and depending on tribe, location and time controlled varying parts of the Maghreb, at times unifying it (as under the Fatimids). The Fatimid Islamic state, also known as Fatimid Caliphate made an Islamic empire that included North Africa, Sicily, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Egypt, the Red Sea coast of Africa, Tihamah, Hejaz and Yemen. Caliphates from Northern Africa traded with the other empires of their time, as well as forming part of a confederated support and trade network with other Islamic states during the Islamic Era.
The Amazighs historically consisted of several tribes. The two main branches were the Botr and Barnès tribes, who were divided into tribes, and again into sub-tribes. Each region of the Maghreb contained several tribes (for example, Sanhadja, Houara, Zenata, Masmouda, Kutama, Awarba, and Berghwata). All these tribes made independent territorial decisions.
Several Amazigh dynasties emerged during the Middle Ages in the Maghreb and other nearby lands. Ibn Khaldun provides a table summarizing the Amazigh dynasties of the Maghreb region, the Zirid, Banu Ifran, Maghrawa, Almoravid, Hammadid, Almohad, Merinid, Abdalwadid, Wattasid, Meknassa and Hafsid dynasties.
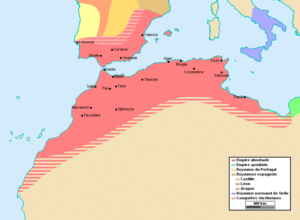
In the early 16th century, Spain constructed fortified outposts (presidios) on or near the Algerian coast. Spain took control of few coastal towns like Mers el Kebir in 1505; Oran in 1509; and Tlemcen, Mostaganem and Ténès in 1510. In the same year, a few merchants of Algiers ceded one of the rocky islets in their harbor to Spain, which built a fort on it. The presidios in North Africa turned out to be a costly and largely ineffective military endeavor that did not guarantee access for Spain’s merchant fleet.
There reigned in Ifriqiya, current Tunisia, a Berber family, Zirid, somehow recognizing the suzerainty of the Fatimid caliph of Cairo. Probably in 1048, the Zirid ruler or viceroy, el-Mu’izz, decided to end this suzerainty. The Fatimid state was too weak to attempt a punitive expedition; The Viceroy, el-Mu’izz, also found another means of revenge.
