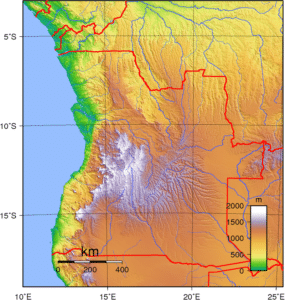
Angola borders Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north-east and the South Atlantic Ocean to the west. The coastal exclave of Cabinda in the north has borders with the Republic of the Congo to the north and with the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south. Angola’s capital, Luanda, lies on the Atlantic coast in the northwest of the country.
Exclave of Cabinda:
With an area of approximately 2,812 square miles, the Northern Angolan province of Cabinda is unusual in being separated from the rest of the country by a strip, some 37 miles wide, of the Democratic Republic of Congo along the lower Congo River. Cabinda borders the Congo Republic to the north and north-northeast and the DRC to the east and south. The town of Cabinda is the chief population centre.
According to a 1995 census, Cabinda had an estimated population of 600,000, approximately 400,000 of whom live in neighbouring countries. Population estimates are, however, highly unreliable. Consisting largely of tropical forest, Cabinda produces hardwoods, coffee, cocoa, crude rubber and palm oil. The product for which it is best known, however, is its oil, which has given it the nickname, “the Kuwait of Africa”. Cabinda’s petroleum production from its considerable offshore reserves now accounts for more than half of Angola’s output. Most of the oil along its coast was discovered under Portuguese rule by the Cabinda Gulf Oil Company (CABGOC) from 1968 onwards.
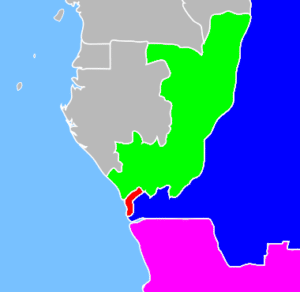
Ever since Portugal handed over sovereignty of its former overseas province of Angola to the local independence groups (MPLA, UNITA and FNLA), the territory of Cabinda has been a focus of separatist guerrilla actions opposing the Government of Angola (which has employed its armed forces, the FAA—Forças Armadas Angolanas) and Cabindan separatists. The Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda-Armed Forces of Cabinda (FLEC-FAC) announced a virtual Federal Republic of Cabinda under the Presidency of N’Zita Henriques Tiago. One of the characteristics of the Cabindan independence movement is its constant fragmentation, into smaller and smaller factions.
Economy:
Angola has diamonds, oil, gold, copper and a rich wildlife (dramatically impoverished during the civil war), forest and fossil fuels. Since independence, oil and diamonds have been the most important economic resource. Smallholder and plantation agriculture dramatically dropped in the Angolan Civil War, but began to recover after 2002. The transformation industry of the late colonial period collapsed at independence, because of the exodus of most of the ethnic Portuguese population, but it has begun to re-emerge with updated technologies, partly because of an influx of new Portuguese entrepreneurs. Similar developments have taken place in the service sector.

Angola’s economy has in recent years moved on from the disarray caused by a quarter-century of Angolan civil war to become the fastest-growing economy in Africa and one of the fastest-growing in the world, with an average GDP growth of 20% between 2005 and 2007. In the period 2001–10, Angola had the world’s highest annual average GDP growth, at 11.1%.
