As part of the Ring of Fire, California is subject to tsunamis, floods, droughts, Santa Ana winds, wildfires, landslides on steep terrain, and has several volcanoes. It has many earthquakes due to several faults running through the state, in particular, the San Andreas Fault. About 37,000 earthquakes are recorded each year, but most are too small to be felt.
Economy:
California’s economy ranks among the largest in the world. As of 2017, the gross state product (GSP) is about $2.75 trillion ($70,000 per capita), the largest in the United States. California is responsible for 13.9 percent of the United States’ approximate $18.1 trillion gross domestic product (GDP). As of 2015, California’s nominal GDP is larger than all but 4 countries (the United States, China, Japan and Germany).
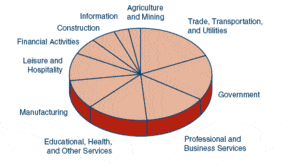
The five largest sectors of employment in California are trade, transportation, and utilities; government; professional and business services; education and health services; and leisure and hospitality. In output, the five largest sectors are financial services, followed by trade, transportation, and utilities; education and health services; government; and manufacturing.
California’s economy is dependent on trade and international related commerce accounts for about one-quarter of the state’s economy. In 2008, California exported $144 billion worth of goods, up from $134 billion in 2007 and $127 billion in 2006. Computers and electronic products are California’s top export, accounting for 42 percent of all the state’s exports in 2008.
Agriculture is an important sector in California’s economy. Farming-related sales more than quadrupled over the past three decades, from $7.3 billion in 1974 to nearly $31 billion in 2004. This increase has occurred despite a 15 percent decline in acreage devoted to farming during the period, and water supply suffering from chronic instability. Factors contributing to the growth in sales-per-acre include more intensive use of active farmlands and technological improvements in crop production. In 2008, California’s 81,500 farms and ranches generated $36.2 billion products revenue. In 2011, that number grew to $43.5 billion products revenue. The Agriculture sector accounts for two percent of the state’s GDP and employs around three percent of its total workforce. According to the USDA in 2011, the three largest California agricultural products by value were milk and cream, shelled almonds, and grapes.

Per capita GDP in 2007 was $38,956, ranking eleventh in the nation. Per capita income varies widely by geographic region and profession. The Central Valley is the most impoverished, with migrant farm workers making less than minimum wage. According to a 2005 report by the Congressional Research Service, the San Joaquin Valley was characterized as one of the most economically depressed regions in the United States, on par with the region of Appalachia. California has a poverty rate of 23.5%, the highest of any state in the country. Many coastal cities include some of the wealthiest per-capita areas in the United States. The high-technology sectors in Northern California, specifically Silicon Valley, in Santa Clara and San Mateo counties, have emerged from the economic downturn caused by the dot-com bust.
