The isolation of the Comoros had made air traffic a major means of transportation. One of President Abdallah’s accomplishments was to make the Comoros more accessible by air. During his administration, he negotiated agreements to initiate or enhance commercial air links with Tanzania and Madagascar. The Djohar regime reached an agreement in 1990 to link Moroni and Brussels by air. By the early 1990s, commercial flights connected the Comoros with France, Mauritius, Kenya, South Africa, Tanzania, and Madagascar. The national airline was Air Comores. Daily flights linked the three main islands, and air service was also available to Mahoré; each island had airstrips. In 1986 the republic received a grant from the French government’s CCCE to renovate and expand Hahaya airport, near Moroni. Because of the absence of scheduled sea transport between the islands, nearly all interisland passenger traffic is by air.

More than 99% of freight is transported by sea. Both Moroni on Njazidja and Mutsamudu on Nzwani have artificial harbors. There is also a harbor at Fomboni, on Mwali. Despite extensive internationally financed programs to upgrade the harbors at Moroni and Mutsamudu, by the early 1990s only Mutsamudu was operational as a deepwater facility. Its harbor could accommodate vessels of up to eleven meters’ draught. At Moroni, ocean-going vessels typically lie offshore and are loaded or unloaded by smaller craft, a costly and sometimes dangerous procedure. Most freight continues to be sent to Kenya, Reunion, or Madagascar for transshipment to the Comoros. Use of Comoran ports is further restricted by the threat of cyclones from December through March. The privately operated Comoran Navigation Company (Société Comorienne de Navigation) is based in Moroni, and provides services to Madagascar.
Roads serve the coastal areas, rather than the interior, and the mountainous terrain makes surface travel difficult.
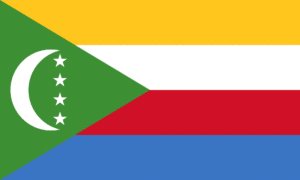
Flag of the Comoros:
The national flag of the Union of the Comoros was designed in 2001 and officially adopted on January 7, 2002. It continues to display the crescent and four stars, which is a motif that has been in use in slightly various forms since 1975 during the independence movement. In its constitution, the government of the Comoros refers to the insignia as l’emblème national, or the “national emblem”, though it is understood to actually represent a flag.
The design consists of a white crescent with four white five-pointed stars inside of a green triangle. The flag has four stripes, representing four islands of the nation: Yellow is for Mohéli, White is for Mayotte (claimed by Comoros but administered by France), Red is for Anjouan, and Blue is for Grande Comore. The four stars on the flag also symbolize the four islands of the Comoros. The star and crescent symbol stands for their main religion, Islam.
The first official flag of Comoros was designed and adopted for local use in 1963 by Suzanne Gauthier, before Comoros gained its independence. It had a white crescent at upper hoist facing the fly, four stars in a diagonal, and used a 5:7 proportion with a green background. This design continued to be used after independence in 1975.