Its slow decline starting at the end of the 14th century followed internal discord and revolts by vassal states, one of which, Songhai, flourished as an empire between the 14th and 16th centuries. Songhai was also weakened by internal discord, which led to factional warfare. This discord spurred most of the migrations southward toward the forest belt. The dense rain forest covering the southern half of the country, created barriers to the large-scale political organizations that had arisen in the north. Inhabitants lived in villages or clusters of villages; their contacts with the outside world were filtered through long-distance traders. Villagers subsisted on agriculture and hunting.
Pre-European Modern Period:
Five important states flourished in Ivory Coast during the pre-European early modern period. The Muslim Kong Empire was established by the Joola in the early 18th century in the north-central region inhabited by the Sénoufo, who had fled Islamization under the Mali Empire. Although Kong became a prosperous center of agriculture, trade, and crafts, ethnic diversity and religious discord gradually weakened the kingdom. In 1895 the city of Kong would be sacked and conquered by Samori Ture of the Wassoulou Empire.
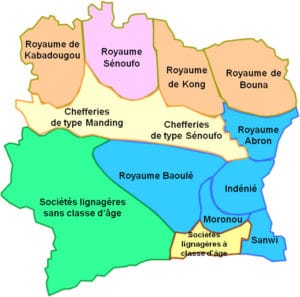
The Abron kingdom of Gyaaman was established in the 17th century by an Akan group, the Abron, who had fled the developing Ashanti confederation of Asanteman in what is present-day Ghana. From their settlement south of Bondoukou, the Abron gradually extended their hegemony over the Dyula people in Bondoukou, who were recent arrivals from the market city of Begho. Bondoukou developed into a major center of commerce and Islam. The kingdom’s Quranic scholars attracted students from all parts of West Africa. In the mid-17th century in east-central Ivory Coast, other Akan groups fleeing the Asante established a Baoulé kingdom at Sakasso and two Agni kingdoms, Indénié and Sanwi.
The Baoulé, like the Ashanti, developed a highly centralized political and administrative structure under three successive rulers. It finally split into smaller chiefdoms. Despite the breakup of their kingdom, the Baoulé strongly resisted French subjugation. The descendants of the rulers of the Agni kingdoms tried to retain their separate identity long after Ivory Coast’s independence; as late as 1969, the Sanwi attempted to break away from Ivory Coast and form an independent kingdom. The current king of Sanwi is Amon N’Douffou V (since 2005).
Establishment of French Rule:
Compared to neighboring Ghana, Ivory Coast, though practicing slavery and slave raiding, suffered little from the slave trade as such. European slave and merchant ships preferred other areas along the coast. The earliest recorded European voyage to West Africa was made by the Portuguese in 1482. The first West African French settlement, Saint Louis, was founded in the mid-17th century in Senegal, while at about the same time, the Dutch ceded to the French a settlement at Goree Island, off Dakar. A French mission was established in 1637 at Assinie near the border with the Gold Coast (now Ghana). The Europeans suppressed the local practice of slavery at this time and forbade the trade to their merchants.
