Among the main tourist destinations are:
Nature attractions: Galápagos Islands, Yasuni National Park, El Cajas National Park, Sangay National Park, Podocarpus National Park, Vilcabamba, Baños de Agua Santa.
Cultural attractions: Historic center of Quito, Ciudad Mitad del Mundo, Ingapirca, Historic center of Cuenca, Latacunga and its Mama Negra festival.
Snowy mountains: Antisana volcano, Cayambe volcano, Chimborazo volcano, Cotopaxi volcano, Illinizas volcanoes.
Beaches: Atacames, Bahía de Caráquez, Crucita, Esmeraldas, Manta, Montañita, Playas, Salinas.
Transportation:
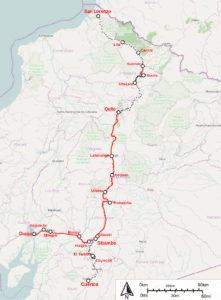
The rehabilitation and reopening of the Ecuadorian railroad and use of it as a tourist attraction is one of the recent developments in transportation matters.
The roads of Ecuador in recent years have undergone important improvement. The major routes are Pan American (under enhancement from four to six lanes from Rumichaca to Ambato, the conclusion of 4 lanes on the entire stretch of Ambato and Riobamba and running via Riobamba to Loja). In the absence of the section between Loja and the border with Peru, there are the Route Espondilus and/or Ruta del Sol (oriented to travel along the Ecuadorian coastline) and the Amazon backbone (which crosses from north to south along the Ecuadorian Amazon, linking most and more major cities of it).
Another major project is developing the road Manta – Tena, the highway Guayaquil – Salinas Highway Aloag Santo Domingo, Riobamba – Macas (which crosses Sangay National Park). Other new developments include the National Unity bridge complex in Guayaquil, the bridge over the Napo river in Francisco de Orellana, the Esmeraldas River Bridge in the city of the same name, and, perhaps the most remarkable of all, the Bahia – San Vincente Bridge, being the largest on the Latin American Pacific coast.
Cuenca’s tramway is the largest public transport system in the city and the first modern tramway in Ecuador. It was inaugurated on March 8, 2019. It has 20,4 km and 27 stations. It will transport 120 000 passagers daily. Its route starts in the south of Cuenca and ends in the north at the Parque Industrial neighbourhood.

The Mariscal Sucre International Airport in Quito and the José Joaquín de Olmedo International Airport in Guayaquil have experienced a high increase in demand and have required modernization. In the case of Guayaquil it involved a new air terminal, once considered the best in South America and the best in Latin America[91] and in Quito where an entire new airport has been built in Tababela and was inaugurated in February 2013, with Canadian assistance. However, the main road leading from Quito city centre to the new airport will only be finished in late 2014, making current travelling from the airport to downtown Quito as long as two hours during rush hour.[92] Quito’s old city-centre airport is being turned into parkland, with some light industrial use.
Flag of Ecuador:
The national flag of Ecuador, which consists of horizontal bands of yellow (double width), blue and red, was first adopted by law in 1835 and later on 26 September 1860. The design of the current flag was finalized in 1900 with the addition of the coat of arms in the center of the flag. Before using the yellow, blue and red tricolor, Ecuador used white and blue flags that contained stars for each province of the country. The design of the flag is very similar to those of Colombia and Venezuela, which are also former constituent territories of Gran Colombia. All three are based on a proposal by Venezuelan General Francisco de Miranda, which was adopted by Venezuela in 1811 and later Gran Colombia with some modifications. There is a variant of the flag that does not contain the coat of arms that is used by the merchant marine. This flag matches Colombia’s in every aspect, but Colombia uses a different design when her merchant marine ships are at sail.
