Introduction:
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of more than seventeen thousand islands, including Sumatra, Java, Borneo (Kalimantan), Sulawesi, and New Guinea (Papua). Indonesia is the world’s largest island country and the 14th largest country by land area, at 1,904,569 square kilometres (735,358 square miles). With over 267 million people, it is the world’s 4th most populous country as well as the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world’s most populous island, is home to more than half of the country’s population.
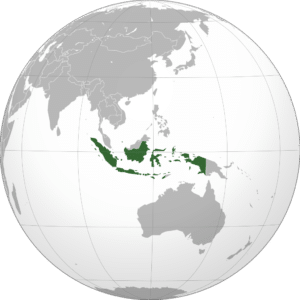
The sovereign state is a presidential, constitutional republic with an elected legislature. It has 34 provinces, of which five have special status. The country’s capital, Jakarta, is the second-most populous urban area in the world. The country shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia. Other neighboring countries include Singapore, Vietnam, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India’s Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Despite its large population and densely populated regions, Indonesia has vast areas of wilderness that support one of the world’s highest levels of biodiversity.
The Indonesian archipelago has been a valuable region for trade since at least the 7th century when Srivijaya and later Majapahit traded with entities from mainland China and the Indian subcontinent. Local rulers gradually absorbed foreign influences from the early centuries and Hindu and Buddhist kingdoms flourished. Sunni traders and Sufi scholars brought Islam, while Europeans introduced Christianity through colonization. Although sometimes interrupted by the Portuguese, French and British, the Dutch were the foremost colonial power for much of their 350-year presence in the archipelago. The concept of “Indonesia” as a nation-state emerged in the early 20th century and the country proclaimed its independence in 1945. However, it was not until 1949 that the Dutch recognized Indonesia’s sovereignty following an armed and diplomatic conflict between the two.
Indonesia consists of hundreds of distinct native ethnic and linguistic groups, with the largest one being the Javanese. A shared identity has developed with the motto “Bhinneka Tunggal Ika” (“Unity in Diversity” literally, “many, yet one”), defined by a national language, ethnic diversity, religious pluralism within a Muslim-majority population, and a history of colonialism and rebellion against it. The economy of Indonesia is the world’s 16th largest by nominal GDP and 7th by GDP at PPP. The country is a member of several multilateral organisations, including the United Nations, World Trade Organization, International Monetary Fund, G20, and a founding member of Non-Aligned Movement, Association of Southeast Asian Nations, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, East Asia Summit, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.
History:
Early History:
Fossilised remains of Homo erectus, popularly known as the “Java Man“, suggest the Indonesian archipelago was inhabited two million to 500,000 years ago. Homo sapiens reached the region around 43,000 BCE. Austronesian peoples, who form the majority of the modern population, migrated to Southeast Asia from what is now Taiwan. They arrived in the archipelago around 2,000 BCE and confined the native Melanesian peoples to the far eastern regions as they spread east. Ideal agricultural conditions and the mastering of wet-field rice cultivation as early as the eighth century BCE allowed villages, towns, and small kingdoms to flourish by the first century CE. The archipelago’s strategic sea-lane position fostered inter-island and international trade, including with Indian kingdoms and Chinese dynasties, from several centuries BCE. Trade has since fundamentally shaped Indonesian history.
