Kenya has a Human Development Index (HDI) of 0.555 (medium), ranked 145 out of 186 in the world. As of 2005, 17.7% of Kenyans lived on less than $1.25 a day. In 2017, Kenya ranked 92nd in the World Bank ease of doing business rating from 113rd in 2016 (of 190 countries). The important agricultural sector is one of the least developed and largely inefficient, employing 75% of the workforce compared to less than 3% in the food secure developed countries. Kenya is usually classified as a frontier market or occasionally an emerging market, but it is not one of the least developed countries.
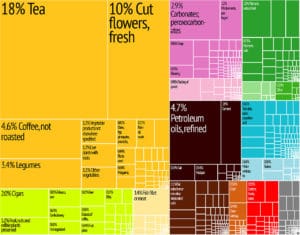
The economy has seen much expansion, seen by strong performance in tourism, higher education, and telecommunications, and decent post-drought results in agriculture, especially the vital tea sector. Kenya’s economy grew by more than 7% in 2007, and its foreign debt was greatly reduced.
Transportation:
According to the Kenya Roads Board, Kenya has 160,886 kilometres (99,970 mi) of roads. Several paving projects are underway.
Two routes in the Trans-African Highway network pass through Kenya and the capital, Nairobi:
The Cairo-Cape Town Highway, Trans-African Highway 4, linking North Africa, East Africa and Southern Africa. From Nairobi southwards this is one of the most heavily used routes in the network, and includes one of the longest complete paved sections. However, it still has missing links to the north and it is not practical to travel to Cairo without off-road vehicles. This part will be completed as part of the LAPSSET project.
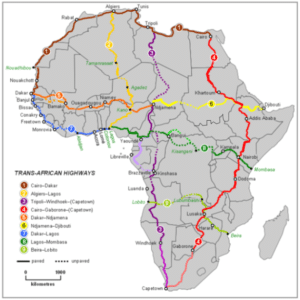
The Lagos-Mombasa Highway, Trans-African Highway 8, links East Africa and West Africa. It is only complete between the Ugandan–DR Congo border and Mombasa, linking the African Great Lakes region to the sea. It is also named the ‘Trans-African Highway’.
There are around 100,000 matatus (minibuses), which constitute the bulk of the country’s public transport system.
Larger and safer bus services are offered by a range of companies throughout the country.
Jomo Kenyatta International Airport in Nairobi, is Kenya’s largest airport and serves the most destinations. Some international flights go to Moi International Airport in Mombasa. Kisumu Airport was upgraded to an international airport in 2011 and a second phase of expansion is under way.

The national company Kenya Railways Corporation runs the former Uganda Railway and its branches in Kenya. The most important line in the country runs between the port of Mombasa and Nairobi, sleeping car accommodation is offered for tourists.
Part of the Lake Victoria system is within the boundaries of Kenya. Kenya has a major international port at Mombasa, serving both Kenya and Uganda. Kisumu on Lake Victoria is also another major port, which has ferry connections to Uganda and Tanzania.
Flag of Kenya:
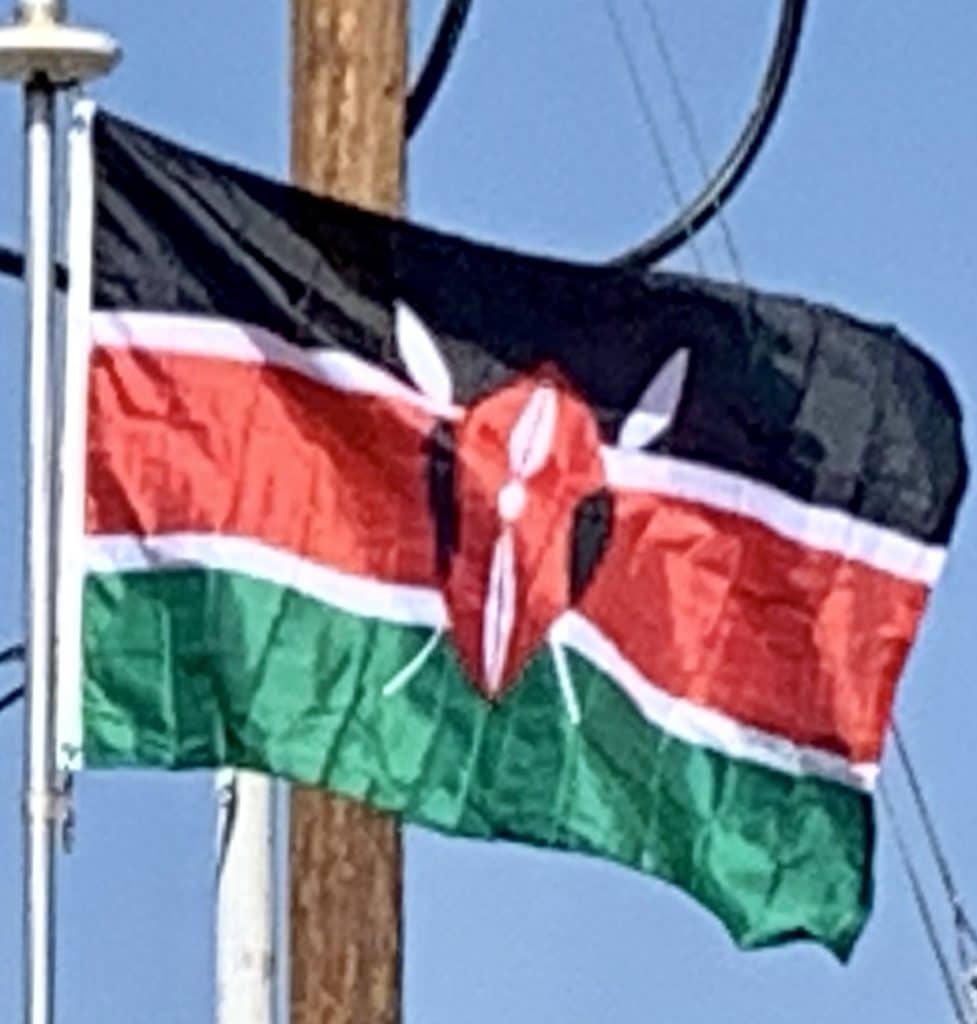
The flag of Kenya is a tricolour of black, red, and green with two white edges imposed with a red, white and black Maasai shield and two crossed spears. The flag is based on that of Kenya African National Union and was officially adopted on 12 December 1963 after Kenya’s independence.
